Securing your home is a significant investment, and understanding the cost of home insurance is crucial for responsible budgeting. This guide delves into the multifaceted world of home insurance premiums, exploring the various factors that influence pricing and offering practical strategies for securing the best value. From location and property condition to coverage levels and personal history, we’ll unpack the key elements that determine how much you’ll pay to protect your most valuable asset.
We’ll navigate the complexities of different policy types, compare obtaining quotes through various methods, and provide actionable tips for saving money on your premiums. Ultimately, this guide aims to empower you with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions about your home insurance, ensuring you have the right coverage at the right price.
Factors Influencing Home Insurance Costs
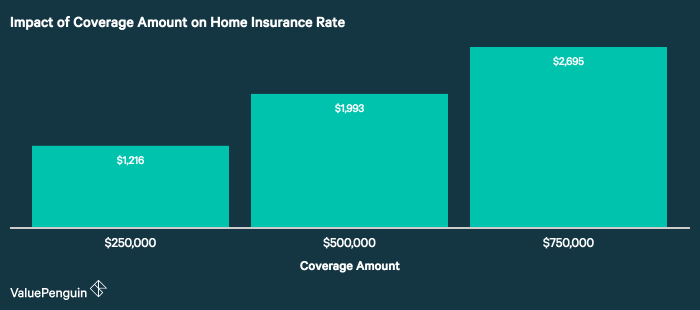
Several key factors significantly impact the cost of home insurance premiums. Understanding these factors can help homeowners make informed decisions and potentially save money. This section will explore the most influential elements, providing examples and illustrative data where possible.
Location’s Impact on Home Insurance Premiums
The location of your home is a primary determinant of your insurance cost. Insurance companies assess risk based on geographical factors like the frequency of natural disasters (hurricanes, earthquakes, wildfires), crime rates, and the prevalence of severe weather events. High-risk areas, such as coastal regions prone to hurricanes or areas with a history of wildfires, will generally command higher premiums due to the increased likelihood of claims. Conversely, low-risk areas in stable, less disaster-prone regions typically have lower premiums. For example, a home in hurricane-prone Florida will likely have a much higher premium than a similar home in a less vulnerable inland state like Iowa. Similarly, a home located in a neighborhood with a high crime rate might face higher premiums due to the increased risk of theft or vandalism.
Age and Condition of a Home
The age and condition of your home directly influence insurance costs. Older homes, especially those lacking modern safety features and updates, are often considered higher risk due to increased potential for damage or failure of older systems. Conversely, newer homes built with modern building codes and materials are usually considered lower risk. The condition of your home, including the state of its roof, plumbing, and electrical systems, also plays a significant role. Regular maintenance and upgrades can help lower your premiums.
| Age | Condition | Estimated Cost (Annual Premium) | Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| New (less than 5 years) | Excellent | $1,000 | Modern construction, updated systems |
| 10-20 years old | Good | $1,200 | Some minor repairs needed |
| 30-40 years old | Fair | $1,500 | Significant repairs needed, outdated systems |
| Over 50 years old | Poor | $2,000+ | Major repairs needed, high risk of system failure |
*Note: These are estimated costs and can vary widely based on other factors.*
Impact of Different Coverage Levels on Premiums
The level of coverage you choose significantly affects your premium. Higher coverage amounts naturally lead to higher premiums, as the insurance company assumes a greater financial responsibility. However, inadequate coverage can leave you financially vulnerable in the event of a major loss. It’s crucial to find a balance between adequate protection and affordability.
| Coverage Type | Coverage Amount | Premium Cost (Annual) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Actual Cash Value (ACV) | $200,000 | $1,000 | Covers the replacement cost minus depreciation. |
| Replacement Cost | $200,000 | $1,200 | Covers the full cost of replacement, regardless of depreciation. |
| Liability Coverage | $300,000 | $200 | Protects you against lawsuits if someone is injured on your property. |
| Comprehensive Coverage | $250,000 | $1,500 | Includes both property and liability coverage, plus additional benefits. |
*Note: These are illustrative examples and actual costs will vary based on location, risk profile, and insurer.*
Homeowner’s Personal History and Insurance Rates
Your personal history as a homeowner significantly influences your insurance rates. Several key factors are considered:
- Claims History: Filing multiple claims in the past can increase your premiums, as it signals a higher risk to the insurer.
- Credit Score: Insurers often use credit scores as an indicator of risk. A lower credit score may result in higher premiums.
- Safety Features: Installing security systems, smoke detectors, and other safety features can lower your premiums by demonstrating a reduced risk profile.
Obtaining Home Insurance Quotes

Securing the best home insurance policy involves careful comparison shopping. This requires obtaining quotes from multiple providers to ensure you find the coverage you need at a competitive price. Understanding the process and different methods available will empower you to make informed decisions.
The process of getting home insurance quotes is straightforward, although the specific steps may vary slightly depending on the provider. Generally, you’ll follow a similar pattern, regardless of whether you apply online, by phone, or in person.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Obtaining Home Insurance Quotes
To effectively compare home insurance quotes, follow these steps:
- Gather Necessary Information: Before contacting any insurer, compile essential details about your property, including its address, square footage, age, construction materials (e.g., brick, wood), and any significant features (e.g., pool, detached garage). Also, prepare information about your personal circumstances, such as your credit history and claims history. Having this ready will expedite the quoting process.
- Contact Multiple Insurers: Reach out to at least three to five different insurance providers. This allows for a wider range of coverage options and price comparisons. Use a mix of methods (online, phone, in-person) to experience the different approaches.
- Complete the Application: Each insurer will require you to complete an application, either online or via a phone interview. Be accurate and thorough in your responses to ensure you receive an accurate quote.
- Compare Quotes Carefully: Once you receive quotes, don’t just focus on the price. Scrutinize the coverage details, deductibles, and any exclusions. A cheaper policy with limited coverage might not be the best value in the long run.
- Select Your Policy: After careful comparison, choose the policy that best suits your needs and budget. Ensure you understand all the terms and conditions before signing the contract.
Comparison of Quote Obtaining Methods
Each method for obtaining quotes offers distinct advantages and disadvantages. Consider these factors when choosing your approach:
- Online: Offers convenience and speed. You can easily compare multiple quotes simultaneously. However, it may lack the personalized assistance available through other methods. Some online tools allow you to instantly see quotes based on entered information.
- Phone: Allows for direct interaction with an insurance agent, providing opportunities for clarification and personalized advice. However, it can be time-consuming to contact multiple agents and gather information.
- In-Person: Provides the most personalized service and allows for detailed discussions about your specific needs. However, it requires more time and effort to visit multiple insurance offices.
Information Typically Requested by Insurance Providers
Insurance companies require comprehensive information to assess risk and determine appropriate premiums. Expect to provide details such as:
- Property details: Address, square footage, age, construction type, number of bedrooms and bathrooms, security systems.
- Coverage needs: Desired coverage amounts for dwelling, personal property, liability, and additional coverages (e.g., flood, earthquake).
- Personal information: Name, address, contact information, date of birth, driver’s license information.
- Claims history: Details of any previous insurance claims, including the date, cause, and amount of the claim.
- Credit information: Many insurers use credit-based insurance scores to assess risk.
Outcome Summary
Protecting your home is a priority, and understanding the intricacies of home insurance is paramount. While the cost can vary significantly based on numerous factors, this guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the key considerations. By carefully evaluating your individual circumstances, comparing quotes from different providers, and implementing cost-saving strategies, you can secure adequate coverage that aligns with your budget and peace of mind. Remember to regularly review and update your policy to ensure it continues to meet your evolving needs.
FAQ
What is a deductible, and how does it affect my premium?
A deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. Higher deductibles generally result in lower premiums, as you’re assuming more of the risk.
Does my credit score impact my home insurance rates?
In many states, your credit score is a factor considered by insurers. A higher credit score often correlates with lower premiums.
How often should I review my home insurance policy?
It’s advisable to review your policy annually, or whenever there’s a significant change in your property or circumstances (e.g., renovations, additions, changes in coverage needs).
Can I get home insurance if I have a previous claim?
Yes, but a previous claim might affect your premium. Insurers assess risk based on your claims history.
What is the difference between actual cash value (ACV) and replacement cost coverage?
ACV coverage pays for the depreciated value of damaged property, while replacement cost coverage pays for the cost of replacing it with new, similar items.