Navigating the world of home insurance can feel like deciphering a complex code, especially when considering the significant variations in rates across different states. This guide unravels the mysteries behind these discrepancies, offering a clear understanding of the factors influencing your premiums and empowering you to make informed decisions. We’ll explore everything from location-specific risks and property characteristics to insurance company practices and strategies for securing the best possible rates.
From understanding the impact of state regulations and natural disaster frequency to leveraging discounts and comparing quotes from multiple insurers, this comprehensive resource equips you with the knowledge to secure affordable and adequate home insurance coverage. We’ll delve into the intricacies of rate setting, risk assessment, and consumer strategies, providing practical insights and actionable advice.
State-Specific Regulations and Their Impact
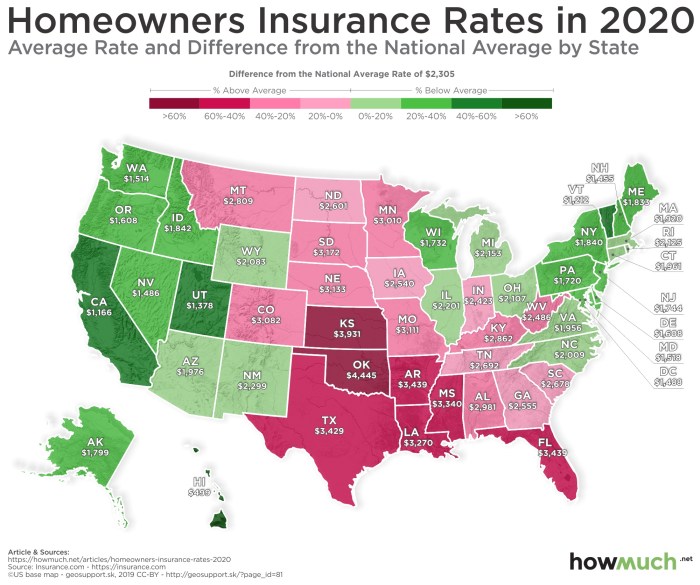
Home insurance rates vary significantly across the United States, and a key driver of this variation is the differing regulatory environments in each state. State-level regulations directly influence the pricing strategies of insurance companies, ultimately affecting the cost of coverage for homeowners. Understanding these regulatory differences is crucial for consumers seeking the best value in home insurance.
State insurance departments play a vital role in regulating the insurance market within their respective jurisdictions. Their oversight ensures fair pricing practices, protects consumers from predatory behavior, and maintains the solvency of insurance companies. This regulatory framework, however, differs substantially from state to state, leading to a complex landscape of insurance costs.
Comparison of Insurance Regulations Across Three States
Three states – Florida, California, and Texas – offer a compelling comparison due to their diverse regulatory approaches and varying exposure to natural disasters. Florida, with its high vulnerability to hurricanes, has a heavily regulated market with strict rules regarding rate increases and coverage requirements. California, also prone to wildfires and earthquakes, has a complex regulatory system balancing consumer protection with the needs of the insurance industry. Texas, meanwhile, has a more deregulated market, allowing insurers greater flexibility in setting rates, but also potentially leading to greater price disparities. These differing regulatory frameworks directly impact the average cost of home insurance in each state. For example, the stringent regulations in Florida might limit the potential for significant rate reductions, while the more open market in Texas could lead to both higher and lower premiums depending on the insurer and the specific risk profile.
The Role of State-Level Insurance Departments in Regulating Rates
State insurance departments are responsible for approving or rejecting rate filings submitted by insurance companies. They use various methods to assess the reasonableness of proposed rates, often considering factors like the insurer’s loss experience, operating expenses, and the risk profile of the insured properties. Some states employ a “prior approval” system, requiring insurers to obtain explicit approval before implementing new rates. Others utilize a “file and use” system, allowing insurers to implement rates after a specified waiting period, unless the department intervenes. Furthermore, state departments conduct market conduct examinations to ensure compliance with regulations and identify potential consumer protection issues. The regulatory approach of a state’s insurance department significantly shapes the competitiveness and pricing dynamics within its home insurance market. For instance, a more stringent prior approval system might lead to lower rates but could also hinder the availability of insurance in high-risk areas.
Impact of Natural Disaster Frequency on Insurance Costs
The frequency and severity of natural disasters significantly influence home insurance rates. States frequently experiencing hurricanes, earthquakes, wildfires, or floods generally have higher average premiums. This is because insurers must factor in the increased risk of claims and potential payouts. For example, Florida’s high hurricane risk leads to substantially higher insurance costs compared to states with lower exposure to such events. Similarly, California’s wildfire risk drives up premiums in vulnerable areas. This correlation between disaster frequency and insurance costs is a key factor in explaining regional variations in home insurance prices. Insurers use sophisticated models to assess risk, incorporating historical data on disaster occurrences and projections for future events, which directly influence the pricing of insurance policies.
States with the Highest and Lowest Average Home Insurance Rates
States with the highest average home insurance rates often coincide with those facing the greatest natural disaster risk or having more stringent regulatory environments. Florida and Louisiana consistently rank among the states with the highest average premiums, largely due to the high frequency of hurricanes. Conversely, states with lower disaster risk and potentially more deregulated markets may have lower average rates. However, it is crucial to note that numerous factors contribute to rate variations, including the age and condition of homes, crime rates, and the availability of competitive insurers in the state. A direct comparison requires considering a multitude of variables beyond simply disaster frequency and regulatory structure. For example, while Midwest states might have lower average rates due to fewer natural disasters, certain regions within those states could still have high premiums due to other factors, such as aging infrastructure or high instances of property theft.
Insurance Company Practices and Rate Setting
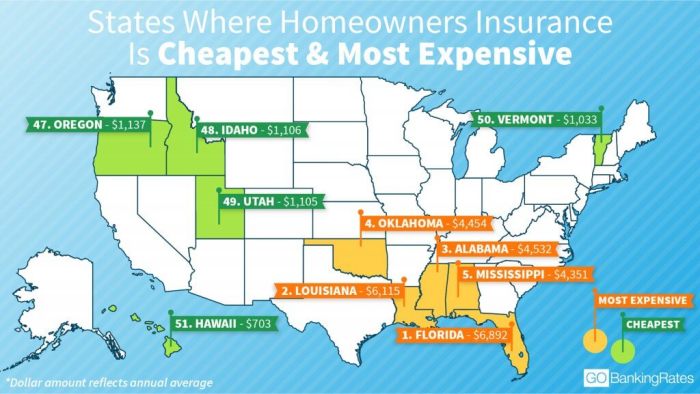
Home insurance rates are not arbitrarily determined; they are the result of a complex process involving various factors and methodologies employed by insurance companies. Understanding these practices is crucial for consumers to make informed decisions about their coverage and to advocate for fair premiums. This section will delve into the rating methodologies of major providers, risk assessment techniques, and the impact of credit scores and claims history.
Rating Methodologies of Major Home Insurance Providers
Three major home insurance providers—let’s call them Provider A, Provider B, and Provider C—employ slightly different rating methodologies, leading to variations in premiums. Provider A heavily emphasizes actuarial models based on historical claims data and geographic location. Their system uses sophisticated algorithms to analyze numerous variables and predict future claims. Provider B incorporates a more subjective approach, using a combination of actuarial modeling and individual risk assessment by underwriters who consider factors such as the age and condition of the home and the presence of security systems. Provider C focuses on a hybrid model, combining advanced statistical analysis with a strong emphasis on credit-based insurance scores. The differences in these methodologies directly influence the final premium calculation. For example, a home in a high-risk area might receive a significantly higher premium from Provider A than from Provider B, if Provider B’s underwriters deem the property itself to be low-risk.
Risk Assessment and Premium Determination
Insurance companies assess risk through a variety of methods. They analyze factors such as the age and condition of the home (roof age, plumbing systems, presence of earthquake-resistant features), the location (proximity to fire hydrants, flood zones, crime rates), and the homeowner’s history (claims history, credit score). For instance, a home with an older roof and located in a wildfire-prone area will likely receive a higher premium than a newer home with a modern roof in a low-risk area. Additionally, the presence of security systems, such as alarms and monitored security cameras, can lead to a lower premium as these systems mitigate the risk of theft or vandalism. The comprehensive assessment of these risk factors allows insurers to develop a more accurate premium reflecting the likelihood of claims.
Influence of Credit Scores and Claims History
Credit scores significantly influence home insurance rates in many states. Insurers often use credit-based insurance scores (CBIS), which are different from traditional credit scores but still reflect financial responsibility. A higher CBIS generally correlates with lower premiums, reflecting the insurer’s belief that financially responsible individuals are less likely to file frivolous claims. Conversely, a low CBIS can result in significantly higher premiums. Claims history is another crucial factor. Filing multiple claims in the past can increase future premiums, as it signals a higher risk profile to the insurer. For example, a homeowner with two or more claims in the past five years might see a substantial increase in their premium compared to a homeowner with a clean claims history.
Impact of Underwriting Practices on Varying Rates
Different underwriting practices across insurance companies lead to varying rates. Some companies may have stricter underwriting guidelines, leading to higher premiums for individuals perceived as higher risk. Other companies may have a more lenient approach, resulting in lower premiums for the same individual. For example, Provider A might refuse to insure homes older than 50 years, while Provider B might insure them but with a higher premium. These differences in risk tolerance and underwriting criteria directly translate into differences in premiums offered to consumers. The level of detail in the underwriting process, the specific factors weighted, and the overall risk appetite of the company all play a significant role in shaping the final premium.
Consumer Considerations and Strategies for Saving Money
Securing affordable home insurance is a crucial aspect of responsible homeownership. Understanding your options and employing smart strategies can significantly reduce your annual premiums. This section details practical steps to lower your costs and find the best coverage for your needs.
Steps to Reduce Home Insurance Costs
Taking proactive measures can lead to considerable savings on your home insurance. These actions demonstrate your commitment to risk mitigation, a key factor in determining your premium.
- Improve your home’s security: Installing security systems, reinforcing doors and windows, and adding exterior lighting can significantly lower your risk profile and, consequently, your premiums. Many insurers offer discounts for these improvements.
- Increase your deductible: A higher deductible means lower premiums. Carefully consider your financial capacity to handle a larger out-of-pocket expense in case of a claim before making this adjustment.
- Maintain your home: Regular maintenance, including roof inspections, plumbing checks, and electrical system upkeep, prevents costly repairs and demonstrates responsible homeownership, leading to lower premiums.
- Shop around and compare quotes: Don’t settle for the first quote you receive. Comparing quotes from multiple insurers is essential to finding the best value for your money.
- Consider discounts: Many insurers offer discounts for various factors, such as being a long-term customer, bundling policies, or belonging to certain organizations. Inquire about all available discounts.
Finding Affordable Home Insurance Options
Finding the right balance between affordability and adequate coverage requires careful research and comparison. The following strategies can assist in your search for affordable home insurance.
- Use online comparison tools: Numerous websites allow you to compare quotes from multiple insurers simultaneously, streamlining the process and saving you time.
- Check with your current insurer: Before switching, contact your current provider to see if they can offer any better rates or discounts.
- Consider regional insurers: Smaller, regional insurers may offer competitive rates, particularly if they specialize in your area.
- Explore different policy types: Different policy types offer varying levels of coverage and cost. Understanding the nuances of each type is crucial for making an informed decision.
Benefits of Bundling Home and Auto Insurance
Bundling your home and auto insurance with the same provider often results in significant savings. This is because insurers reward loyalty and efficiency by offering bundled discounts.
For example, a family might save 10-15% or more on their combined premiums by bundling their home and auto insurance, compared to purchasing separate policies from different companies. These savings can accumulate significantly over time.
Comparing Quotes from Multiple Insurers
Obtaining quotes from multiple insurers is paramount to securing the most competitive rates. This comparative approach ensures you are not overpaying for your coverage.
It is recommended to get at least three to five quotes from different insurers to get a comprehensive understanding of the market and the range of available prices and coverage options.
Appealing a Home Insurance Rate Increase
If your insurer increases your rates, you have the right to appeal the decision. Clearly articulate your reasons for contesting the increase, providing supporting evidence such as home improvements or a history of claim-free years.
Many insurers have a formal appeals process. Review your policy and contact your insurer’s customer service department to understand the steps involved in filing an appeal. Document all communications and keep records of any supporting evidence you submit.
Final Review
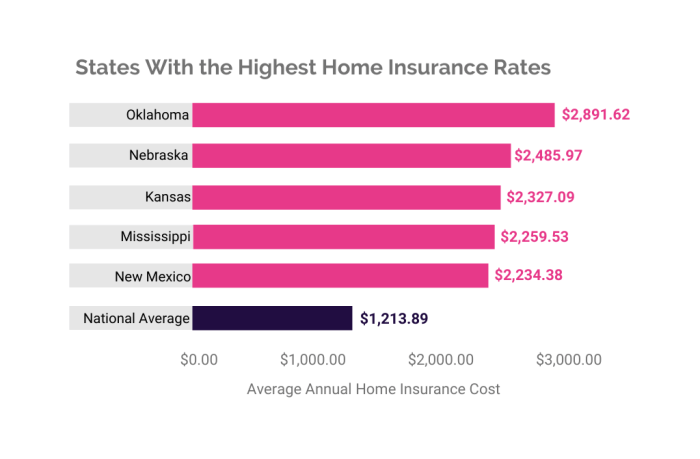
Ultimately, securing affordable yet comprehensive home insurance requires a multifaceted approach. By understanding the interplay of location, property features, coverage levels, insurer practices, and state regulations, homeowners can effectively navigate the insurance landscape. This guide serves as a valuable resource, empowering you to make informed choices and secure the best possible protection for your most valuable asset. Remember, proactive comparison shopping, understanding your risk profile, and exploring available discounts are key to achieving significant savings without compromising on coverage.
FAQ Corner
What is the average cost of home insurance in the US?
The average cost varies significantly by state and depends on numerous factors. There’s no single national average that’s truly representative.
How often are home insurance rates reviewed?
Rates are typically reviewed annually, and adjustments are made based on various factors, including claims experience, inflation, and changes in risk assessments.
Can I get home insurance if I have a poor credit score?
Yes, but a poor credit score may lead to higher premiums. Insurers often consider credit scores as an indicator of risk.
What is the difference between actual cash value (ACV) and replacement cost coverage?
ACV covers the replacement cost minus depreciation, while replacement cost covers the full cost of replacing damaged property without accounting for depreciation.
What does liability coverage in home insurance protect me against?
Liability coverage protects you financially if someone is injured on your property or if your actions cause damage to someone else’s property.