Homeownership represents a significant investment, a cornerstone of financial stability, and a haven for cherished memories. Protecting this investment requires careful consideration, and at the heart of that protection lies home insurance. This guide delves into the intricacies of home insurance, exploring its various facets, from understanding policy components to navigating the claims process and securing the best coverage for your needs. We’ll equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions and safeguard your most valuable asset.
From defining the core elements of a home insurance policy to exploring the nuances of different coverage types and the factors influencing premiums, this comprehensive guide aims to demystify the process of securing adequate home insurance. We will also provide practical tips for comparing quotes, understanding policy renewals, and implementing preventative measures to minimize risk and maintain a secure and comfortable home.
Defining Home Insurance

Home insurance is a crucial financial safety net, protecting homeowners from significant financial losses resulting from unforeseen events that could damage their property or cause them liability. It’s a contract between a homeowner and an insurance company, where the company agrees to compensate the homeowner for covered losses in exchange for regular premium payments. This protection extends beyond the physical structure of the house itself, encompassing a range of potential risks.
Home insurance policies typically include several key features designed to provide comprehensive coverage. These features are tailored to the specific needs and circumstances of the policyholder, offering varying levels of protection and customization options. The core purpose is to mitigate the financial burden associated with unexpected damage or legal liabilities.
Types of Home Insurance Coverage
Different types of coverage are available to address various potential risks associated with homeownership. Understanding these distinctions is vital for selecting a policy that adequately protects your assets and financial well-being.
- Dwelling Coverage: This protects the physical structure of your home, including the foundation, walls, roof, and attached structures, against damage from covered perils such as fire, windstorms, and hail. The coverage amount is typically based on the replacement cost of your home.
- Liability Coverage: This protects you from financial responsibility if someone is injured on your property or if you accidentally damage someone else’s property. Liability coverage can cover legal fees and medical expenses resulting from such incidents.
- Personal Property Coverage: This covers your belongings inside your home, such as furniture, clothing, electronics, and jewelry, against loss or damage from covered perils. This coverage often includes additional living expenses if your home becomes uninhabitable due to a covered event.
- Other Structures Coverage: This extends protection to detached structures on your property, such as a garage, shed, or fence, against damage from covered perils.
- Medical Payments Coverage: This covers medical expenses for guests who are injured on your property, regardless of whether you are legally liable.
Factors Influencing Home Insurance Premiums
Several factors contribute to the cost of your home insurance premiums. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions and potentially secure more favorable rates.
- Location: Homes in areas prone to natural disasters (e.g., hurricanes, earthquakes, wildfires) typically command higher premiums due to the increased risk.
- Home Value: The replacement cost of your home is a significant factor. Higher-value homes generally require higher premiums to cover potential losses.
- Coverage Amount: The amount of coverage you choose directly impacts your premium. Higher coverage amounts naturally lead to higher premiums.
- Deductible: A higher deductible (the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in) typically results in lower premiums. Conversely, a lower deductible leads to higher premiums.
- Credit Score: In many jurisdictions, your credit score can influence your insurance premiums. A higher credit score often translates to lower premiums.
- Claim History: A history of filing insurance claims can lead to higher premiums, reflecting an increased risk assessment by the insurer.
- Type of Home: The age, construction materials, and features of your home can also influence your premium. For instance, a home with updated fire safety features might receive a lower rate.
Understanding Policy Components
A standard home insurance policy is a complex legal document, but understanding its key components is crucial for ensuring you’re adequately protected. This section breaks down the typical structure and highlights important aspects to consider. Familiarizing yourself with these elements will empower you to make informed decisions about your coverage.
A typical home insurance policy is structured in several sections, each addressing a specific aspect of coverage. These sections often include details about the insured property, the coverage provided, exclusions, and conditions. The policy will clearly define the responsibilities of both the insurer and the insured. It’s essential to carefully review each section to understand what is and isn’t covered.
Policy Sections and Clauses
Standard home insurance policies typically include sections covering dwelling coverage (the structure of your home), personal property coverage (your belongings), liability coverage (protection against lawsuits), and additional living expenses (coverage for temporary housing if your home becomes uninhabitable). Each section will contain specific clauses detailing the extent of coverage, conditions, and limitations. For example, the dwelling coverage section might specify the valuation method used (e.g., replacement cost or actual cash value) and any limitations on coverage for specific types of damage (e.g., flood or earthquake).
Policy Exclusions and Limitations
Understanding what your policy *doesn’t* cover is just as important as understanding what it *does* cover. All home insurance policies have exclusions – specific events or circumstances that are not covered. Common exclusions include damage caused by floods, earthquakes, and acts of war. Limitations restrict the amount of coverage provided for certain items or events. For example, there might be a limit on the amount of coverage for jewelry or other high-value items. Failing to understand these exclusions and limitations could leave you financially vulnerable in the event of a covered loss.
Comparison of Policy Features
Different insurance providers offer varying levels of coverage and policy features. Comparing policies from multiple providers is essential to finding the best value for your needs. The following table illustrates a simplified comparison; always refer to the policy documents for precise details.
| Insurance Provider | Dwelling Coverage | Personal Property Coverage | Liability Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Provider A | Replacement Cost | Actual Cash Value | $300,000 |
| Provider B | Actual Cash Value | Replacement Cost | $500,000 |
| Provider C | Replacement Cost | Replacement Cost | $250,000 |
Factors Affecting Insurance Costs
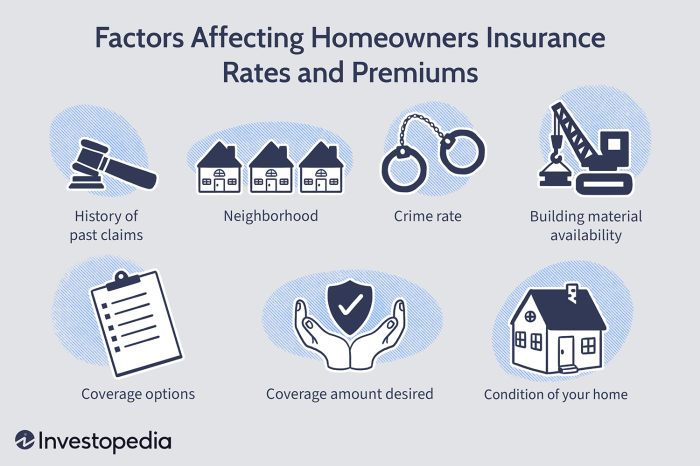
Several key factors influence the cost of home insurance premiums. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions when choosing a policy and potentially save money. Insurance companies use a complex algorithm considering numerous variables to assess risk and set premiums accordingly.
Insurance companies meticulously analyze various aspects of your property and your circumstances to determine the level of risk they are assuming. This risk assessment directly translates into the premium you pay. A higher perceived risk results in a higher premium, while a lower risk leads to a lower premium. This is a fundamental principle of insurance.
Key Factors Determining Home Insurance Premiums
The following factors significantly impact your home insurance costs. It’s important to note that the relative weight of each factor can vary depending on the insurer and the specific circumstances.
- Location: Your home’s location plays a crucial role. Areas prone to natural disasters (earthquakes, hurricanes, floods, wildfires) will command higher premiums due to the increased risk. Similarly, high-crime areas often lead to increased premiums because of a greater chance of theft or vandalism. For example, a home in a coastal region susceptible to hurricanes will typically have a much higher premium than a similar home located inland.
- Age and Condition of the Home: Older homes, especially those lacking modern safety features (updated electrical systems, plumbing, roofing), are generally considered higher risk and thus more expensive to insure. Regular maintenance and upgrades can help mitigate these costs. A well-maintained, recently renovated home will usually attract lower premiums than a neglected older property.
- Coverage Amount: The amount of coverage you choose directly affects your premium. Higher coverage amounts mean higher premiums, as the insurer is assuming a greater financial responsibility. It’s crucial to find a balance between adequate coverage and affordability, considering the replacement cost of your home and its contents.
- Deductible Amount: Your deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. Choosing a higher deductible generally lowers your premium, as you’re taking on more financial responsibility. Conversely, a lower deductible leads to a higher premium.
- Credit Score: In many jurisdictions, your credit score is a factor in determining your insurance rates. A higher credit score often correlates with a lower premium, reflecting a perceived lower risk of non-payment.
- Home Security Features: Homes equipped with security systems (alarms, security cameras) are often considered lower risk and may qualify for discounts. These features can deter burglars and potentially reduce the likelihood of claims.
- Type of Home Construction: The materials used in your home’s construction can influence premiums. Homes built with fire-resistant materials, for example, might receive lower rates than those constructed with more flammable materials.
Cost Differences Between Home Insurance Policies
Different types of home insurance policies offer varying levels of coverage and, consequently, different price points. Understanding these differences is essential for selecting the right policy for your needs.
- Basic Coverage: This provides fundamental protection against damage to the structure of your home and liability for injuries on your property. It’s generally the most affordable option but offers limited coverage.
- Broad Coverage: This expands upon basic coverage, adding protection against more perils, such as falling objects or damage from ice and snow. It typically costs more than basic coverage but provides greater protection.
- Comprehensive Coverage: This offers the most extensive protection, covering a wide range of perils and often including additional features like liability coverage for specific situations or additional living expenses during repairs. This is the most expensive option but offers the most comprehensive protection.
Shopping for Home Insurance
Finding the right home insurance policy can feel overwhelming, but a systematic approach can simplify the process and ensure you secure the best coverage at a competitive price. This involves comparing quotes, carefully reviewing policy documents, and assessing the insurer’s financial strength.
Comparing home insurance quotes from different providers is crucial for securing the most favorable terms. Different insurers utilize varying calculation methods and offer diverse coverage options, resulting in a wide range of premiums. A thorough comparison allows you to identify the policy that best balances coverage and cost.
Comparing Home Insurance Quotes
To effectively compare quotes, gather several quotes from different insurers. Use online comparison tools to streamline the process, but remember to verify the information provided independently. Pay close attention not only to the premium but also to the deductible, coverage limits, and any exclusions. Consider factors like the insurer’s reputation and financial stability, as these are equally important in determining the long-term value of your policy. For example, you might find one insurer offers a lower premium, but their coverage limits are significantly lower than a slightly more expensive competitor. Carefully weigh these trade-offs.
Careful Review of Policy Documents
Before committing to a home insurance policy, thoroughly review the policy document. This document Artikels the specifics of your coverage, including what is and is not covered, the limits of liability, and the conditions under which claims will be paid. Pay close attention to exclusions, which specify situations or types of damage not covered by the policy. Understanding these details is crucial to avoid unpleasant surprises in the event of a claim. For instance, a standard policy may exclude flood damage, requiring separate flood insurance. Understanding these exclusions helps you make informed decisions about supplemental coverage.
Assessing Insurer Financial Stability and Reputation
The financial stability and reputation of an insurance company are critical considerations. A financially sound insurer is more likely to be able to pay claims when needed. You can assess an insurer’s financial strength by checking independent rating agencies such as A.M. Best, Moody’s, and Standard & Poor’s. These agencies assign ratings based on the insurer’s financial health and ability to meet its obligations. Additionally, research the insurer’s reputation by looking at online reviews and customer testimonials. Websites like the Better Business Bureau can also provide insights into an insurer’s track record in handling customer complaints. For example, an insurer with a consistently high rating from multiple agencies and positive customer reviews demonstrates greater reliability than one with lower ratings or numerous complaints.
Understanding Policy Renewals
Your home insurance policy doesn’t last forever. Understanding the renewal process is crucial for maintaining adequate coverage and avoiding unexpected costs. Renewal typically involves a review of your policy, assessment of your risk profile, and potentially, an adjustment to your premium.
Policy renewal is usually a straightforward process. Most insurers will send you a renewal notice several weeks before your policy expires, outlining the new premium and any changes to your coverage. You’ll typically have a grace period to review the terms and pay the renewed premium. Failure to pay within this period may result in your coverage lapsing. It’s essential to review the renewal notice carefully to ensure the information is accurate and reflects your current needs and circumstances. For instance, if you’ve made significant home improvements or changes to your property, you should inform your insurer to ensure your coverage adequately reflects these changes.
Premium Changes During Renewal
Premiums can fluctuate during renewal due to several factors. These factors include changes in your risk profile (e.g., claims history, upgrades to security systems), changes in the insurer’s pricing models, and broader economic factors such as inflation and increased claims payouts in your area. For example, if you’ve filed a claim in the past year, your premium might increase to reflect the increased risk you pose to the insurer. Conversely, installing a security system could lead to a premium reduction. Similarly, a period of increased natural disasters in your region might cause insurers to adjust their pricing across the board. It’s important to understand that premium changes are common and often reflect the ongoing assessment of risk.
Options When Unhappy with Policy or Premium
If you’re unhappy with your renewal premium or the terms of your policy, you have several options. You can contact your insurer to discuss your concerns and explore potential ways to lower your premium. This might involve increasing your deductible or bundling your home insurance with other policies, such as auto insurance. Alternatively, you can shop around for a new policy with a different insurer. Comparing quotes from multiple insurers can help you find a policy that better suits your needs and budget. Remember to carefully compare the coverage offered by different insurers before making a decision. Finally, you could consider negotiating with your current insurer; they may be willing to offer a more competitive price to retain your business. It’s always advisable to explore all available options before deciding on a course of action.
Ending Remarks
Ultimately, securing adequate home insurance is not merely a financial transaction; it’s an investment in peace of mind. By understanding the complexities of home insurance policies, diligently comparing options, and proactively managing risk, homeowners can protect their investment, their belongings, and their future. This guide serves as a foundational resource, empowering you to navigate the world of home insurance with confidence and ensure your home remains a sanctuary for years to come.
Q&A
What is the difference between actual cash value (ACV) and replacement cost coverage?
ACV coverage pays for the current market value of damaged property, minus depreciation. Replacement cost coverage pays for the cost of replacing the damaged property with new, similar items, without deducting for depreciation.
How often should I review my home insurance policy?
It’s advisable to review your policy annually, or whenever there’s a significant change in your property (renovations, additions) or your personal circumstances (increased valuable possessions).
What happens if I don’t make a claim for a minor incident?
Not making a claim for minor incidents usually won’t affect your future premiums, unless it becomes a pattern suggesting a higher risk profile. However, always check your policy details.
Can I get home insurance if I have a previous claim?
Yes, but insurers may consider your claims history when setting your premium. Be upfront about past claims when applying for new coverage.