Securing your home is a significant investment, and understanding the associated costs is crucial. Home insurance premiums are far from uniform; they’re a complex tapestry woven from various factors, ranging from your location’s risk profile to the specific features of your property and the level of coverage you choose. This guide unravels the intricacies of home insurance cost, empowering you to make informed decisions and potentially save money.
We’ll explore the key elements influencing your premiums, from geographical location and property characteristics to the type of policy and your personal risk profile. Understanding these factors allows you to navigate the insurance landscape effectively, securing the best possible coverage at a price that aligns with your budget. We’ll also delve into strategies for finding affordable options and negotiating favorable terms with insurers.
Factors Influencing Home Insurance Costs
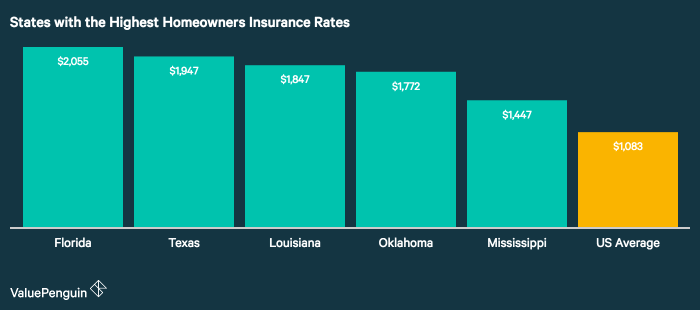
Understanding the factors that determine your home insurance premium is crucial for securing the best coverage at a reasonable price. Several key elements contribute to the final cost, and being aware of these can help you make informed decisions about your policy and potentially lower your premiums.
Location’s Impact on Home Insurance Premiums
Your home’s location significantly influences your insurance cost. Areas prone to natural disasters like hurricanes, earthquakes, wildfires, or floods command higher premiums due to increased risk for insurers. Similarly, high-crime areas may also lead to higher premiums due to a greater likelihood of theft or vandalism. The following table illustrates this variation across different risk zones:
| Location | Average Premium | Factors Contributing to Premium | Example Insurance Provider |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coastal Area (High Hurricane Risk) | $2,500 | High risk of hurricane damage, flooding | Example Insurer A |
| Suburban Area (Low Risk) | $1,200 | Low crime rate, minimal natural disaster risk | Example Insurer B |
| Urban Area (High Crime Rate) | $1,800 | High theft and vandalism rates | Example Insurer C |
| Rural Area (High Wildfire Risk) | $1,900 | Proximity to wildfire-prone areas | Example Insurer D |
Age and Condition of the Home
Older homes, particularly those lacking modern safety features and updated building materials, typically carry higher insurance premiums than newer homes. This is because older structures may be more vulnerable to damage from storms, fires, or other hazards. Regular maintenance and updates, such as replacing outdated plumbing or electrical systems, can help mitigate these risks and potentially lower your premiums. A thorough home inspection by your insurer may influence the final premium based on identified risks. For instance, a home with a leaky roof or outdated electrical wiring might be deemed a higher risk.
Influence of Different Coverage Options
The types of coverage you choose directly impact your premium. Liability coverage, which protects you against lawsuits if someone is injured on your property, is usually a mandatory component. Dwelling coverage protects the structure of your home, while personal property coverage protects your belongings inside. Comprehensive coverage encompassing all these aspects, along with additional options like flood or earthquake insurance, will naturally result in a higher premium compared to a more basic policy. The level of coverage you select for each aspect directly correlates to the overall cost. For example, opting for higher coverage limits for dwelling and personal property will increase the premium.
Impact of Home Security Systems and Safety Features
Installing home security systems, such as alarm systems, smoke detectors, and fire sprinklers, can significantly reduce your insurance premiums. These features demonstrate a commitment to mitigating risk, leading insurers to view your property as less hazardous and thus, less expensive to insure. Many insurers offer discounts for homes equipped with such safety measures. For instance, a discount of 5-10% is common for homes with monitored security systems. Similarly, features like impact-resistant windows and reinforced doors can also lead to premium reductions.
Impact of External Factors on Home Insurance Costs
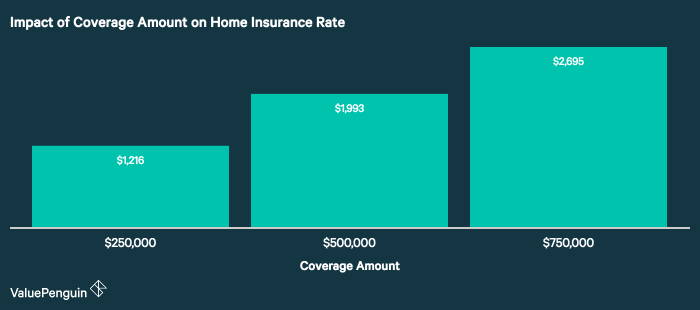
Home insurance premiums are not solely determined by factors related to your individual property. A range of external forces significantly influence the cost of your coverage, impacting both the risk assessment undertaken by insurers and their overall operational landscape. Understanding these external factors is crucial for homeowners seeking to manage their insurance expenses effectively.
Natural Disasters and Premiums
The frequency and severity of natural disasters, such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and wildfires, directly correlate with home insurance premiums. Areas prone to these events face higher premiums due to the increased risk insurers assume. For example, coastal regions frequently hit by hurricanes typically have significantly higher insurance costs than inland areas. Similarly, regions situated near fault lines or in wildfire-prone forests experience elevated premiums to reflect the heightened risk of damage and associated payouts. Insurers utilize sophisticated risk models that incorporate historical data on disaster occurrences, projected climate change impacts, and geographical vulnerability to assess and price risk accurately. A recent increase in the frequency and intensity of wildfires in California, for instance, has led to substantial premium increases in affected areas.
Inflation and Economic Conditions
Inflation and broader economic conditions play a crucial role in shaping home insurance costs. Rising inflation increases the cost of repairing or rebuilding homes after damage, directly impacting insurance payouts. Consequently, insurers adjust premiums upward to account for these increased costs. Furthermore, economic downturns can impact the insurance industry’s profitability, potentially leading to premium increases as insurers strive to maintain financial stability. Conversely, periods of economic growth might, in some instances, lead to slightly lower premiums due to increased competition and a greater pool of insured properties. For example, the period of high inflation in the early 1980s led to significant increases in home insurance premiums across the United States.
Insurance Company Profitability and Market Competition
The financial health and competitive dynamics within the home insurance market influence pricing. Profitable insurance companies may have more leeway to offer slightly lower premiums, while those facing financial challenges might need to increase premiums to improve their bottom line. Conversely, a highly competitive market can drive down premiums as companies vie for customers. Conversely, a market with limited competition might result in higher premiums due to reduced pressure to offer lower prices. The level of regulation within a given jurisdiction also impacts the competitive landscape and, consequently, premium pricing.
Credit Score and Insurance Rates
Many insurance companies use credit scores as a factor in determining home insurance rates. A higher credit score often correlates with a lower premium, reflecting the perceived lower risk associated with individuals demonstrating responsible financial behavior. This is because individuals with good credit scores tend to be more financially stable and are less likely to file fraudulent claims. Conversely, those with poor credit scores might face higher premiums, as insurers perceive them as higher-risk clients. The precise impact of credit score on insurance rates varies by insurer and jurisdiction, but it is a significant factor for many companies. The rationale behind this practice is that a poor credit history might suggest a higher likelihood of late payments or other financially irresponsible behaviors, which could increase the risk for the insurer.
Conclusive Thoughts
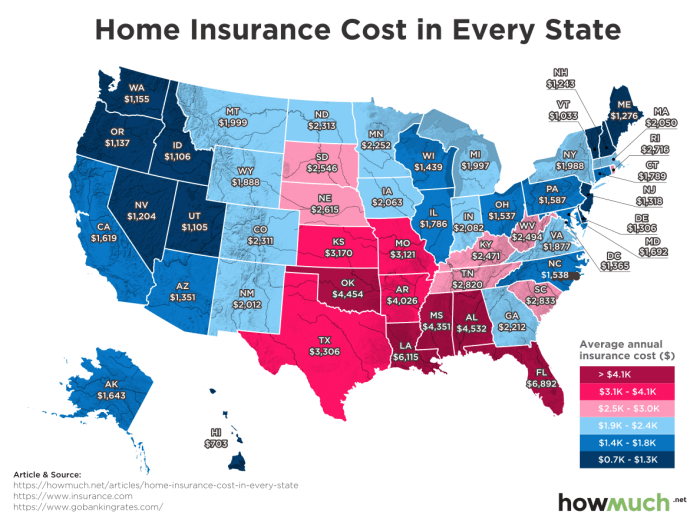
Navigating the world of home insurance can feel overwhelming, but with a clear understanding of the factors that influence costs and the strategies for securing affordable coverage, you can confidently protect your most valuable asset. Remember to carefully compare quotes, understand your policy’s details, and proactively manage your risk to minimize premiums while maximizing protection. By taking a proactive approach, you can ensure your home is adequately insured at a price that fits comfortably within your financial plan.
General Inquiries
What is the difference between actual cash value (ACV) and replacement cost coverage?
ACV coverage pays for the depreciated value of damaged property, while replacement cost coverage pays for the cost of replacing the item with a new one, regardless of depreciation.
How often can I expect my home insurance rates to change?
Rates can change annually, or even mid-term, based on factors like claims experience, changes in your property, or market conditions. Review your policy regularly.
Can I bundle my home and auto insurance for a discount?
Yes, many insurers offer discounts for bundling home and auto insurance policies. This is a common strategy to save money.
What is a deductible, and how does it affect my premiums?
A deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. A higher deductible typically results in lower premiums, but you’ll pay more in the event of a claim.