Homeownership represents a significant investment, both financially and emotionally. Protecting this investment requires a comprehensive understanding of the risks involved and the insurance coverage available to mitigate them. This guide delves into the intricacies of home hazard insurance, exploring its definition, coverage details, claims processes, and preventative measures. We aim to equip you with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions about protecting your home and your peace of mind.
From unexpected weather events to unforeseen accidents, numerous hazards can threaten the structural integrity and contents of your home. Home hazard insurance plays a crucial role in safeguarding against these risks, providing financial protection in the event of damage or loss. By understanding the nuances of policy coverage, exclusions, and claim procedures, homeowners can navigate the complexities of insurance and ensure adequate protection for their most valuable asset.
Defining Home Hazard Insurance

Home hazard insurance, often a component of a broader homeowners or renters insurance policy, protects you from financial losses resulting from unforeseen events that damage your property or possessions. Its purpose is to provide financial compensation to repair or replace damaged items, mitigating the significant costs associated with unexpected hazards. The scope of coverage varies depending on the specific policy and chosen add-ons, but generally aims to safeguard your investment in your home and its contents.
Home hazard insurance is designed to cover a range of perils that could cause damage to your property.
Types of Hazards Typically Covered
A standard home hazard insurance policy typically covers a variety of hazards, although specific coverage can vary by insurer and policy. Common examples include damage caused by fire, windstorms, hail, lightning, explosions, smoke, vandalism, and theft. Some policies may also extend coverage to less frequent events like falling objects, water damage from plumbing failures, or even damage caused by certain types of animals. It’s crucial to review your policy documents carefully to understand the specific hazards covered and any exclusions.
Differences Between Home Hazard Insurance and Other Types of Home Insurance
Home hazard insurance is not a standalone product but rather a component within broader home insurance policies. It’s important to distinguish it from homeowners insurance and renters insurance. Homeowners insurance is a comprehensive package that typically includes hazard coverage along with liability protection (covering injuries or damages caused to others on your property) and additional living expenses (covering temporary housing costs if your home becomes uninhabitable due to a covered event). Renters insurance, on the other hand, focuses primarily on protecting your personal belongings and providing liability coverage, with hazard coverage typically limited to damage to your personal property within the rental unit.
Comparison of Home Insurance Types
| Feature | Home Hazard Insurance (Component) | Homeowners Insurance | Renters Insurance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage Type | Property damage from specific hazards | Property damage, liability, additional living expenses | Personal property damage, liability |
| Property Covered | Structure and/or contents (depending on policy) | Structure, contents, and liability | Personal belongings, liability |
| Target Audience | Homeowners and renters (as part of a broader policy) | Homeowners | Renters |
| Liability Coverage | Usually not included independently | Included | Included |
Coverage Details and Exclusions
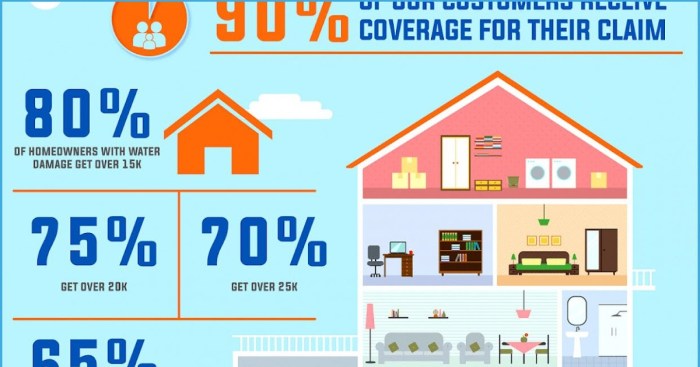
Understanding the specifics of your home hazard insurance policy is crucial. This section details what’s typically covered, what’s usually excluded, and the factors influencing your premium. Knowing this information empowers you to make informed decisions about your coverage.
Home hazard insurance, often referred to as homeowner’s insurance, provides financial protection against various unforeseen events that could damage your property or cause personal liability. A typical policy covers a range of perils, but it’s vital to understand both the inclusions and exclusions to avoid unpleasant surprises in the event of a claim.
Covered Events and Damages
Standard home hazard insurance policies typically cover damage caused by a wide array of events. These can include, but are not limited to, fire, windstorms, hail, lightning strikes, explosions, and vandalism. In addition to property damage, many policies also cover liability for injuries or damages that occur on your property. For instance, if someone slips and falls on your icy walkway and is injured, your liability coverage might help pay for their medical bills and legal expenses. Further, many policies offer coverage for theft and certain types of water damage (excluding flood damage, usually requiring separate flood insurance).
Common Exclusions
While home hazard insurance offers extensive coverage, certain events and damages are typically excluded. These exclusions are often specified in the policy documents. Common exclusions include damage caused by floods, earthquakes, and acts of war. Furthermore, normal wear and tear, insect infestations, and intentional damage caused by the homeowner are generally not covered. Specific exclusions can vary significantly between insurance providers and policy types, highlighting the importance of carefully reviewing your policy wording.
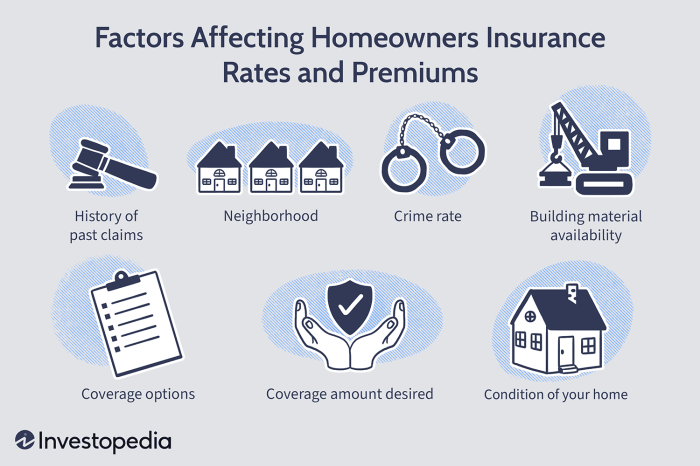
Factors Influencing Premium Costs
Several factors contribute to the cost of your home hazard insurance premiums. The primary factors include the location of your home (areas prone to natural disasters tend to have higher premiums), the age and condition of your home (older homes with outdated systems might cost more to insure), the value of your home and its contents (higher value properties generally result in higher premiums), and your claims history (a history of claims can lead to increased premiums). Other factors, such as the type of coverage you choose (higher coverage limits typically mean higher premiums) and the deductible you select (higher deductibles usually result in lower premiums), also play a significant role.
Deductibles and Coverage Limits
Understanding your deductible and coverage limits is essential for determining your out-of-pocket expenses in the event of a claim. The deductible is the amount you must pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. For example, if your deductible is $1,000 and you have $5,000 in damages, you would pay the first $1,000, and your insurance would cover the remaining $4,000. Coverage limits refer to the maximum amount your insurance company will pay for a specific covered event. It’s important to choose coverage limits that adequately protect the value of your home and belongings. For instance, if your home is valued at $300,000, selecting a coverage limit of $200,000 would leave you significantly underinsured in case of a major loss.
Filing a Claim
Filing a home hazard insurance claim can seem daunting, but understanding the process can make it significantly smoother. This section Artikels the steps involved, necessary documentation, damage assessment, and potential challenges you might encounter. Remember to always refer to your specific policy documents for detailed instructions and requirements.
Claim Reporting Procedures
Promptly reporting your claim is crucial. Most insurers have a 24/7 claims hotline or online portal. Contact them as soon as it is safe to do so after the hazardous event. Provide them with your policy number, a brief description of the incident, and the extent of the damage. They will then guide you through the next steps, potentially assigning a claims adjuster to your case.
Required Documentation
Supporting your claim with comprehensive documentation is vital for a swift and successful resolution. This documentation helps verify the event and the extent of the damage. Examples include:
- Police report (if applicable, such as in cases of theft or vandalism).
- Photographs and videos documenting the damage to your property, both inside and outside.
- Repair estimates from qualified contractors. These should be detailed and itemized.
- Inventory of damaged or lost items, including purchase receipts or appraisals where available. This is particularly important for high-value items.
- Proof of ownership for the property and any damaged items.
Damage Assessment and Payout Determination
Once you’ve reported your claim and submitted the necessary documentation, an insurance adjuster will be assigned to assess the damage. They will inspect your property, review the documentation you provided, and determine the extent of the covered damages. The payout amount will be based on the terms of your policy, the assessed damage, and any applicable deductibles. The adjuster will prepare a detailed report outlining their findings and the recommended payout. You have the right to review this report and negotiate if you disagree with the assessment. Remember, the insurer’s responsibility is limited to the coverage Artikeld in your policy.
Step-by-Step Claim Handling Guide
Navigating the claims process can involve several steps and potential delays. Here’s a guide to help you:
- Report the incident immediately to your insurer.
- Secure your property to prevent further damage. This might involve boarding up windows or covering damaged areas.
- Document the damage thoroughly with photos, videos, and written descriptions.
- Gather all necessary documentation as listed above.
- Cooperate fully with the insurance adjuster’s investigation.
- Review the adjuster’s report carefully and address any discrepancies promptly.
- Understand your policy’s limitations and what is covered.
Potential Delays and Challenges
Claims processing can be subject to delays due to various factors, including:
- High claim volume following a widespread disaster.
- Difficulties in contacting witnesses or obtaining necessary documentation.
- Disputes over the extent of the damage or coverage.
- The need for extensive repairs or rebuilding, which can take considerable time.
Addressing these potential challenges proactively, by maintaining thorough records and communicating effectively with your insurer, can help minimize delays and frustrations.
Last Point
Securing adequate home hazard insurance is a proactive step towards safeguarding your investment and mitigating potential financial burdens arising from unforeseen events. By carefully reviewing policy details, understanding coverage limitations, and implementing preventative measures, you can significantly reduce risks and enhance your preparedness. Remember, a well-informed approach to home hazard insurance empowers you to protect your home and secure your future.
Detailed FAQs
What is the difference between home hazard insurance and homeowners insurance?
The terms are often used interchangeably, but “homeowners insurance” is a broader term encompassing various coverages, including hazard insurance. Hazard insurance specifically addresses damage from perils like fire, wind, and hail.
Does home hazard insurance cover flooding?
Standard home hazard insurance policies typically exclude flood damage. Separate flood insurance is usually required for coverage against flood-related losses.
How long does it take to process a home hazard insurance claim?
Processing times vary depending on the insurer and the complexity of the claim. It can range from a few days to several weeks or even months for extensive damage.
What factors affect my home hazard insurance premium?
Premiums are influenced by factors such as your location, the age and condition of your home, the coverage amount, your deductible, and your claims history.
Can I cancel my home hazard insurance policy at any time?
Generally, yes, but you may be subject to cancellation fees or penalties depending on your policy terms and the insurer’s rules.