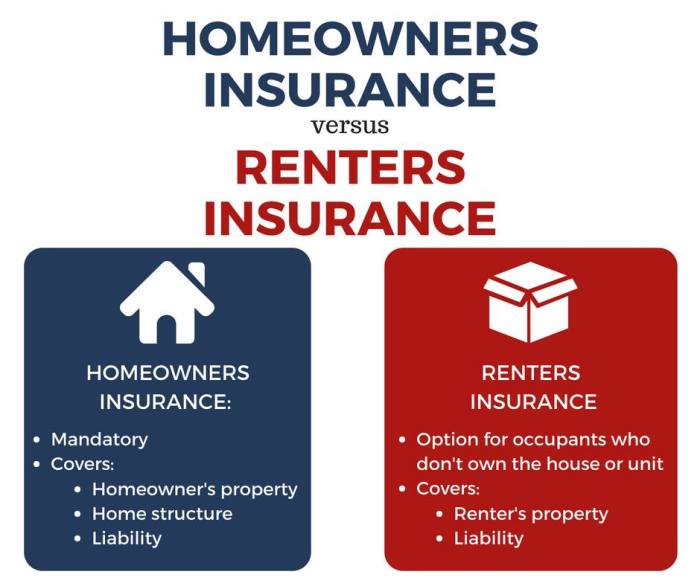
Securing your belongings and protecting yourself from unforeseen circumstances is a cornerstone of responsible adulthood. This guide delves into the often-misunderstood world of home and renters insurance, clarifying the key differences, coverages, and considerations for both homeowners and renters. We’ll explore how to choose the right policy, file a claim effectively, and understand the factors influencing your premiums, ensuring you’re adequately protected.
Whether you’re a first-time renter navigating the complexities of insurance for the first time or a seasoned homeowner looking to optimize your coverage, this guide provides a clear and concise overview of the essential aspects of home and renters insurance, empowering you to make informed decisions about protecting your most valuable assets.
Factors Affecting Insurance Premiums
Understanding the factors that influence your home and renters insurance premiums is crucial for securing the best coverage at a price you can afford. Insurance companies utilize a complex system of risk assessment to determine these premiums, considering various aspects of your property, your lifestyle, and your location.
Key Factors in Home Insurance Premiums
Several key factors determine the cost of your home insurance. These factors help insurers assess the likelihood of a claim and the potential cost of that claim. A higher perceived risk translates to a higher premium.
- Home Value: The higher the value of your home, the more it will cost to rebuild or repair it in the event of damage. Therefore, higher home values generally lead to higher premiums.
- Location: Areas prone to natural disasters (hurricanes, earthquakes, wildfires) or high crime rates will command higher premiums due to the increased risk of claims.
- Coverage Amount: The amount of coverage you choose will directly impact your premium. More comprehensive coverage, including higher liability limits, will generally result in a higher premium.
- Deductible: A higher deductible (the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance kicks in) will typically result in a lower premium. This is because you are assuming more of the financial risk.
- Home Features: Features such as a security system, fire alarms, and updated plumbing can lower your premium by demonstrating a reduced risk of loss.
- Credit Score: In many states, your credit score is a factor in determining your insurance premium. A higher credit score is often associated with lower premiums.
- Age and Condition of the Property: Older homes may require higher premiums due to increased risk of wear and tear and potential issues with outdated systems. Poor home maintenance can also lead to higher premiums.
Key Factors in Renters Insurance Premiums
Renters insurance premiums are determined using a different set of factors, focused on the contents of your apartment and your liability.
- Location: Similar to home insurance, location plays a significant role, with higher-risk areas leading to higher premiums.
- Coverage Amount: The amount of coverage you choose for your personal belongings will affect your premium. More coverage means a higher premium.
- Deductible: As with home insurance, a higher deductible will result in a lower premium.
- Credit Score: Similar to home insurance, your credit score can impact your renters insurance premium in many states.
Comparison of Factors Influencing Home and Renters Insurance Premiums
Both home and renters insurance premiums are influenced by location and credit score. However, home insurance premiums are heavily influenced by the value, age, and condition of the property itself, while renters insurance focuses on the value of the renter’s personal belongings and liability coverage.
Credit Score’s Impact on Insurance Premiums
Insurance companies often use credit scores as an indicator of risk. Individuals with higher credit scores are generally considered lower risk and may qualify for lower premiums. This is because a good credit score often reflects responsible financial behavior, which is seen as a positive predictor of responsible home or apartment maintenance and a lower likelihood of filing fraudulent claims.
Location’s Effect on Insurance Costs
Location is a critical factor in determining insurance premiums for both homeowners and renters. Areas with higher rates of theft, vandalism, or natural disasters will generally have higher insurance costs. For example, homes located in coastal areas prone to hurricanes will likely have significantly higher premiums than homes in inland areas. Similarly, apartments in high-crime neighborhoods will typically command higher renters insurance premiums.
Impact of Property Age and Condition on Insurance Premiums
The age and condition of a property significantly impact home insurance premiums. Older homes may have outdated plumbing or electrical systems, increasing the risk of damage and resulting in higher premiums. Similarly, poor maintenance can lead to increased risk and higher costs. For example, a home with a neglected roof is more likely to sustain damage during a storm, resulting in a higher premium compared to a well-maintained home with a recently replaced roof.
Choosing the Right Coverage

Selecting the appropriate home or renters insurance coverage is crucial for protecting your assets and financial well-being. Understanding your policy’s limits and available options ensures you have adequate protection in the event of unforeseen circumstances. Failing to do so could leave you financially vulnerable in the face of a loss.
Understanding Coverage Limits
Coverage limits define the maximum amount your insurance company will pay for a covered loss. These limits are typically expressed as dollar amounts for different aspects of your policy, such as liability, dwelling coverage (for homeowners), personal property coverage, and additional living expenses. It’s essential to review these limits carefully and ensure they align with the actual value of your belongings and the potential costs associated with liability claims. For example, a homeowner with a valuable collection of art should ensure their personal property coverage limit is high enough to replace those items in case of theft or damage. Similarly, a homeowner who hosts frequent gatherings should consider higher liability limits to protect themselves against potential lawsuits resulting from accidents on their property. Understanding these limits is paramount to avoiding a shortfall in the event of a claim.
Determining Appropriate Liability Coverage
Liability coverage protects you against financial responsibility for bodily injury or property damage caused to others. Determining the appropriate level requires considering several factors, including your lifestyle, assets, and potential risks. A higher liability limit offers greater protection, shielding you from potentially devastating financial consequences. Factors to consider include whether you own a swimming pool, have pets, or frequently entertain guests. For example, a homeowner with a pool might opt for a higher liability limit to account for potential accidents involving children. Similarly, individuals with high net worth might choose a higher limit to protect their assets in case of a significant liability claim. Generally, it’s advisable to choose a liability limit that is significantly higher than your net worth, ensuring sufficient protection against substantial claims.
Benefits of Supplemental Coverage Options
While standard home and renters insurance policies provide essential coverage, supplemental options can enhance protection and address specific needs. These add-ons provide coverage for situations not included in the basic policy, offering greater peace of mind. The cost of these add-ons is generally relatively low compared to the potential financial impact of an uncovered loss. It’s important to carefully review available options and select those that best address your individual circumstances and risk profile.
Examples of Supplemental Coverage Options
Several supplemental coverage options are available, tailored to different needs. These include:
- Identity theft protection: Covers costs associated with restoring your identity after a theft.
- Flood insurance: Provides coverage for damage caused by flooding, typically excluded from standard policies.
- Earthquake insurance: Covers damage caused by earthquakes, often a separate policy.
- Scheduled personal property coverage: Provides specific coverage for high-value items, such as jewelry or antiques, exceeding the standard policy limits.
- Water backup and sump pump coverage: Protects against damage from sewer backups or sump pump failures.
Actual Cash Value vs. Replacement Cost
Understanding the difference between “actual cash value” (ACV) and “replacement cost” is crucial when filing a claim. ACV considers depreciation, meaning the payout reflects the item’s current value, minus depreciation. Replacement cost, on the other hand, covers the cost of replacing the damaged item with a new one of similar kind and quality, without deducting for depreciation. For example, if a five-year-old sofa is damaged, ACV would pay the current value of a used sofa, while replacement cost would cover the cost of a brand-new sofa. Most policies offer replacement cost coverage for personal property, but it’s often subject to a deductible and may have limits. It’s crucial to understand your policy’s specifics to avoid unexpected financial burdens after a loss.
Final Review
Understanding home and renters insurance is crucial for safeguarding your financial well-being. By carefully considering your individual needs, comparing policy options, and understanding the intricacies of coverage, you can secure peace of mind knowing your possessions and liability are adequately protected. Remember to regularly review your policy and adjust coverage as your circumstances change to maintain optimal protection.
Common Queries
What is the difference between actual cash value and replacement cost?
Actual cash value (ACV) compensates you for the depreciated value of your damaged property, while replacement cost covers the full cost of replacing the item with a new one, regardless of its age.
How does my credit score affect my insurance premiums?
Insurance companies often use credit scores as an indicator of risk. A higher credit score typically translates to lower premiums, reflecting a lower perceived risk of claims.
What are some common exclusions in home and renters insurance policies?
Common exclusions include damage caused by floods, earthquakes, and acts of war. Specific exclusions vary by policy, so reviewing your policy document carefully is essential.
Can I file a claim for minor damage?
While you can file a claim for minor damage, it’s important to weigh the cost of the damage against your deductible. Filing frequent claims for small amounts can negatively impact your future premiums.
What documents do I need when filing a claim?
You will generally need proof of ownership, photos or videos of the damage, police reports (if applicable), and detailed descriptions of the incident and the damaged property.
