Securing your home is a significant investment, and understanding the nuances of hazard home insurance is crucial for peace of mind. This guide delves into the complexities of hazard home insurance, exploring its coverage, cost factors, and the steps to selecting the right policy. We’ll examine what’s covered, what’s excluded, and how you can proactively mitigate risks to protect your most valuable asset.
From defining the core concept and comparing it to other home insurance types to outlining preventative measures and illustrating real-world claim scenarios, this comprehensive resource aims to empower homeowners with the knowledge to make informed decisions about their insurance needs.
Factors Affecting Hazard Home Insurance Premiums
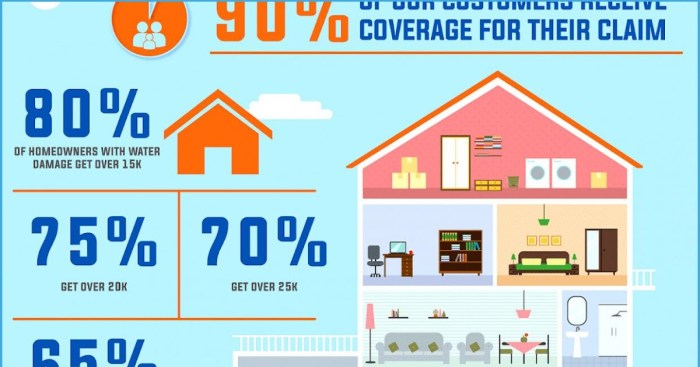
Understanding the factors that influence your home insurance premiums is crucial for securing the best possible coverage at a reasonable price. Several key elements contribute to the final cost, and being aware of these can help you make informed decisions about your home and insurance choices. This section details the major factors insurance companies consider.
Location’s Impact on Premiums
The location of your home significantly impacts your insurance premium. Properties in areas prone to natural disasters, such as hurricanes, earthquakes, wildfires, or floods, will generally command higher premiums due to the increased risk of damage. For instance, a home situated in a coastal region with a history of hurricanes will likely have a higher premium than a similar home located inland. Similarly, homes built in areas with high crime rates may also attract higher premiums due to the increased risk of theft or vandalism. Insurance companies use sophisticated risk assessment models, often incorporating historical data on claims and disaster events, to determine the risk associated with a particular location. This risk assessment directly translates into the premium you pay.
Age and Condition of the Home
The age and condition of your home are also key factors. Older homes, especially those lacking modern safety features like updated electrical wiring or plumbing, are generally considered riskier and may incur higher premiums. Insurance companies assess the structural integrity of the home, considering factors such as the roof’s condition, foundation stability, and the presence of any significant repairs or renovations. Homes with significant wear and tear, or those that haven’t undergone regular maintenance, are more likely to require costly repairs after a covered event, thus increasing the premium. Conversely, well-maintained homes with recent upgrades often qualify for lower premiums as they present a reduced risk of damage. A recent appraisal or home inspection report can help substantiate the condition of your property and potentially influence your premium.
Additional Factors Influencing Premiums
Several other factors contribute to the calculation of your home insurance premium. It’s important to understand these factors to fully appreciate the cost of your coverage.
- Coverage Amount: The higher the coverage amount you choose, the higher your premium will be. This is directly proportional to the potential payout the insurer might have to make in case of a claim.
- Deductible Amount: Choosing a higher deductible, meaning the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in, typically results in lower premiums. This is because you are accepting more financial responsibility in the event of a claim.
- Credit Score: In many jurisdictions, your credit score can influence your insurance premium. A higher credit score often indicates lower risk, potentially leading to lower premiums. This is because a good credit score is often associated with responsible financial behavior.
- Home Security Features: Homes equipped with security systems, such as alarms or security cameras, may qualify for discounts. These features deter theft and vandalism, reducing the insurer’s risk.
- Insurance History: Your past claims history plays a significant role. A history of frequent claims might lead to higher premiums, reflecting the increased risk associated with your insurance profile.
- Type of Construction: The materials used to construct your home can affect the premium. Homes built with fire-resistant materials, for example, may receive a discount.
Mitigation and Prevention Strategies

Proactive measures significantly impact your home insurance premiums. By reducing the likelihood of claims, you demonstrate responsible homeownership, leading to potential discounts and lower overall costs. Understanding and implementing preventative strategies is key to protecting your investment and your wallet.
Implementing preventative measures not only reduces the risk of damage but also demonstrates responsible homeownership to your insurance provider. This responsible approach can translate into lower premiums and greater peace of mind.
Home Improvements That Reduce Premiums
Several home improvements can significantly lower your insurance premiums. These improvements demonstrate a commitment to risk mitigation, making your home a less attractive target for claims. Insurance companies often offer discounts for features that enhance safety and security. For example, installing a modern security system with monitored alarms can substantially reduce your premium. Similarly, upgrading to impact-resistant windows and doors, which are more resistant to break-ins and severe weather, is another worthwhile investment. Finally, improvements that enhance fire safety, such as installing smoke detectors on every level and a fire suppression system, are often rewarded with premium reductions.
Regular Home Inspections and Maintenance
Regular home inspections and maintenance are crucial for identifying and addressing potential hazards before they escalate into costly repairs or damage. A professional inspection can pinpoint issues like faulty wiring, plumbing leaks, or roof damage that might otherwise go unnoticed. Addressing these problems promptly prevents minor issues from becoming major, expensive problems. Furthermore, consistent maintenance, such as cleaning gutters, inspecting the foundation, and checking for pest infestations, helps prevent damage and extends the lifespan of your home’s components. This proactive approach reduces the risk of significant claims, potentially resulting in lower insurance premiums and fewer unexpected expenses.
Actionable Steps to Mitigate Hazards
Taking proactive steps to mitigate hazards is essential for protecting your home and lowering your insurance costs. Here’s a list of actionable steps:
- Install and maintain smoke detectors and carbon monoxide detectors on every level of your home, testing them regularly.
- Regularly inspect and clean gutters and downspouts to prevent water damage to your foundation and roof.
- Trim trees and shrubs around your house to reduce the risk of damage during storms.
- Upgrade to impact-resistant windows and doors to enhance security and protection against severe weather.
- Install a monitored security system to deter burglars and provide rapid response in emergencies.
- Regularly inspect your roof for damage and schedule necessary repairs promptly.
- Ensure proper ventilation in attics and crawl spaces to prevent moisture buildup and mold growth.
- Schedule annual professional home inspections to identify and address potential problems early.
- Maintain your landscaping to reduce fire hazards near your home.
- Protect your home from flooding by installing sump pumps and ensuring proper drainage around your foundation.
End of Discussion

Protecting your home from unforeseen hazards requires a proactive approach and a thorough understanding of your insurance policy. By carefully considering the factors influencing premiums, understanding policy limitations, and implementing preventative measures, you can significantly reduce risks and ensure you have the right coverage in place. Remember to regularly review your policy and compare quotes to ensure you maintain optimal protection for your investment.
Key Questions Answered
What is the difference between hazard insurance and standard homeowners insurance?
Standard homeowners insurance typically covers perils like fire and theft. Hazard insurance often focuses on specific, geographically-concentrated risks like floods or earthquakes, which might be excluded from standard policies and require separate coverage.
How often should I review my hazard home insurance policy?
It’s advisable to review your policy annually, or whenever significant changes occur, such as home renovations or changes in your risk profile (e.g., moving to a higher-risk area).
Can I get hazard insurance if I rent my home?
Renters insurance typically covers your personal belongings, but hazard insurance specific to the property itself is usually the responsibility of the homeowner or landlord. Check with your insurance provider to confirm.
What documentation do I need to file a hazard insurance claim?
You will generally need proof of ownership, detailed documentation of the damage (photos, videos), and a completed claim form provided by your insurance company. Specific requirements vary by provider.