Securing the best homeowners insurance rates requires careful consideration of various factors. This guide navigates the complexities of finding affordable yet comprehensive coverage, exploring key elements impacting premiums and offering practical strategies for securing the most favorable deals. Understanding these factors empowers homeowners to make informed decisions, protecting their most valuable asset.
From evaluating your home’s features and location to comparing quotes from multiple insurers, we’ll unravel the process, providing insights into policy types, coverage details, and potential cost-saving measures. We aim to demystify the insurance landscape, enabling you to confidently navigate the search for the optimal balance of protection and affordability.
Factors Influencing Homeowners Insurance Rates
Securing the best homeowners insurance rate involves understanding the various factors insurance companies consider. These factors are not equally weighted, and some carry significantly more influence than others. This understanding empowers you to make informed decisions about your home and coverage to potentially lower your premiums.
Several key elements contribute to the final cost of your homeowners insurance. These include aspects of your property, your personal circumstances, and the risk the insurance company perceives in insuring your home. A comprehensive understanding of these factors is crucial for securing the most favorable rates.
Home Location
Your home’s location plays a pivotal role in determining your insurance premiums. High-risk areas prone to natural disasters, such as hurricanes, earthquakes, wildfires, or floods, will command higher premiums due to the increased likelihood of claims. For instance, a home situated in a coastal region susceptible to hurricanes will generally have a higher insurance cost than a similar home located inland. Conversely, a home in a low-risk area with a low crime rate will usually attract lower premiums. Insurance companies utilize sophisticated risk assessment models that incorporate historical data on claims frequency and severity for specific geographic locations.
Age and Condition of the Home
Older homes, particularly those lacking modern safety features, are typically considered higher risk. Factors such as the age of the roof, plumbing, electrical systems, and the overall condition of the structure significantly impact the premium. A home with a newer roof and updated electrical system will likely receive a more favorable rate than one with outdated and potentially hazardous components. Regular maintenance and upgrades can demonstrably reduce your insurance costs by mitigating the risk of costly repairs or replacements. A thorough home inspection can identify potential issues and help you make improvements to lower your premiums.
Coverage Amounts
The amount of coverage you choose directly impacts your premium. Higher coverage amounts, while providing greater financial protection in the event of a loss, naturally lead to higher premiums. Conversely, choosing lower coverage amounts may result in lower premiums but leaves you with less financial protection should a significant event occur. It’s crucial to strike a balance between adequate coverage and affordability, considering your home’s value and personal financial situation. For example, underinsuring your home could leave you with significant out-of-pocket expenses in the event of a major loss.
Credit Score Impact
In many states, your credit score is a significant factor in determining your homeowners insurance rate. A higher credit score generally translates to lower premiums, reflecting the insurer’s assessment of your financial responsibility. Insurers view individuals with good credit scores as less risky, assuming they are more likely to pay their premiums on time and are less prone to filing fraudulent claims. Conversely, a poor credit score can result in significantly higher premiums. Improving your credit score can be a proactive step towards reducing your homeowners insurance costs.
Claims History
Your past claims history significantly influences your insurance rates. Filing multiple claims, especially for significant events, can lead to higher premiums. Insurers view frequent claims as an indicator of increased risk. Maintaining a clean claims history demonstrates responsible homeownership and can contribute to lower premiums. For example, a homeowner with no claims in the past five years is likely to receive a more favorable rate than one with multiple claims.
| Factor | Relative Importance | Example of Impact | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Home Location | High | Coastal home vs. inland home | Choose a lower-risk location |
| Age & Condition | High | Outdated plumbing vs. new system | Regular maintenance and upgrades |
| Coverage Amount | High | $500,000 vs. $300,000 coverage | Choose appropriate coverage level |
| Credit Score | Medium-High | 750 credit score vs. 600 credit score | Improve credit score |
| Claims History | Medium | No claims vs. multiple claims | Preventative maintenance |
Types of Homeowners Insurance Coverage
Choosing the right homeowners insurance policy is crucial for protecting your most valuable asset. Understanding the different types of coverage available is essential to ensure you have adequate protection against potential losses. This section will Artikel the key features of several common policy types, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses.
Homeowners insurance policies are categorized by number, such as HO-3, HO-5, and others. These numbers represent different levels and types of coverage. The most common types offer varying degrees of protection for your dwelling, other structures, personal property, and liability. Understanding the nuances of each policy is key to making an informed decision.
HO-3 Coverage
The HO-3, or “Special Form,” is the most widely purchased homeowners insurance policy. It provides open-peril coverage for your dwelling and other structures, meaning it covers damage from almost any cause except those specifically excluded in the policy (like floods or earthquakes). Personal property is covered on a named-peril basis, meaning only damage from specifically listed perils is covered. This policy offers a good balance of coverage and affordability. For example, if a tree falls on your house during a storm, the damage would likely be covered under the open-peril dwelling coverage. However, if a valuable painting is damaged by a sudden power surge, it might only be covered if that specific peril is included in the named-peril section for personal property.
HO-5 Coverage
The HO-5, or “Comprehensive Form,” offers the broadest coverage available. Both your dwelling and personal property are covered on an open-peril basis, providing protection against a wider range of events. This policy is ideal for homeowners who want maximum protection and peace of mind, although it typically comes with a higher premium than an HO-3 policy. For instance, if a fire damages your home and your belongings, the HO-5 would cover both, regardless of the specific cause of the fire. This contrasts with the HO-3, where personal property damage from fire is only covered if it’s explicitly listed as a covered peril in that section of the policy.
HO-8 Coverage
The HO-8, or “Modified Coverage Form,” is designed for older homes that may be difficult to insure under standard policies due to their age or condition. It typically provides named-peril coverage for both the dwelling and personal property, meaning only damage from specifically listed events is covered. This policy offers a more limited scope of coverage compared to HO-3 and HO-5 policies. A situation where an HO-8 might be suitable is for a homeowner living in a historic home with unique architectural features that might be challenging to replace in the event of damage. The coverage may be limited, but it provides some level of protection for such a property.
Key Differences Between Common Homeowners Insurance Policy Types
The following table summarizes the key differences between three common homeowners insurance policy types, allowing for a clearer understanding of the coverage provided by each.
| Policy Type | Dwelling Coverage | Personal Property Coverage | Typical Premium |
|---|---|---|---|
| HO-3 (Special Form) | Open Peril | Named Peril | Moderate |
| HO-5 (Comprehensive Form) | Open Peril | Open Peril | High |
| HO-8 (Modified Coverage Form) | Named Peril | Named Peril | Low to Moderate |
Finding the Best Deals on Homeowners Insurance

Securing the best homeowners insurance rate requires a proactive approach and a thorough understanding of the market. By employing several strategies and carefully comparing options, you can significantly reduce your annual premiums without compromising necessary coverage. This involves leveraging online tools, directly contacting insurers, and understanding your own risk profile to negotiate favorable terms.
Finding the lowest homeowners insurance rate often involves more than simply selecting the first quote you receive. A strategic approach, combining multiple methods, is key to achieving significant savings. The following sections detail effective strategies for securing the best possible deal.
Comparing Quotes from Multiple Insurers
Obtaining quotes from several insurance providers is crucial for identifying the most competitive rates. Different companies utilize varying algorithms and risk assessments, leading to significant price disparities for similar coverage. By comparing at least three to five quotes, you gain a comprehensive understanding of the market and increase your chances of finding a substantially lower premium. Remember to ensure that the coverage offered by each insurer is comparable before making a decision based solely on price.
Utilizing Online Comparison Tools
Online comparison websites offer a convenient way to gather multiple quotes simultaneously. These platforms allow you to input your information once and receive quotes from numerous insurers, simplifying the comparison process. While convenient, it’s essential to review the individual insurer’s policy details directly, as online aggregators may not present the full picture of coverage options or exclusions. Some websites may prioritize insurers with whom they have affiliate agreements, potentially influencing the order of presented quotes.
Negotiating with Insurers
Once you have identified a few competitive quotes, don’t hesitate to negotiate. Highlighting your positive claims history, home security features (like alarm systems or impact-resistant windows), or bundling your homeowners and auto insurance policies can be effective bargaining chips. Being prepared to switch insurers if a better offer isn’t presented can also strengthen your negotiating position. Remember to be polite but firm, clearly stating your expectations and the competitive offers you’ve received.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Comparing Homeowners Insurance Quotes
- Gather Necessary Information: Compile details about your property, including its square footage, age, location, construction materials, and any upgrades or security features. Also, have your current policy details readily available for comparison.
- Utilize Online Comparison Tools: Use at least two or three different online comparison websites to gather a broad range of quotes. Note that the results might vary slightly across platforms.
- Contact Insurers Directly: Follow up with insurers whose quotes initially interest you to clarify coverage details and potentially negotiate a better rate. Ask specific questions about policy exclusions and coverage limits.
- Compare Coverage Details Carefully: Don’t focus solely on price; ensure the coverage offered by each insurer aligns with your needs and risk tolerance. Pay attention to deductibles, coverage limits, and any exclusions.
- Negotiate: Use the quotes you’ve received as leverage to negotiate lower premiums with your preferred insurers. Highlight any positive factors, such as a clean claims history or home security improvements.
- Review Policy Documents: Before finalizing your decision, carefully review the policy documents from your chosen insurer to ensure complete understanding of the terms and conditions.
Understanding Policy Details and Exclusions
Protecting your home is a significant investment, and understanding your homeowners insurance policy is crucial to ensuring you have the right coverage. A thorough review of your policy documents is essential to avoid unexpected costs and ensure you’re adequately protected in case of unforeseen events. Failing to understand the specifics can lead to significant financial burdens should a claim arise.
Carefully reviewing your policy documents will allow you to understand the extent of your coverage, identify potential gaps, and make informed decisions about your insurance needs. This includes clarifying coverage limits, deductibles, and, importantly, exclusions. Knowing what is and isn’t covered prevents unpleasant surprises during a claim process.
Coverage Limits, Deductibles, and Exclusions
Coverage limits define the maximum amount your insurance company will pay for a covered loss. Deductibles represent the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. Exclusions specify events or situations your policy doesn’t cover. For example, a standard policy might exclude damage caused by floods or earthquakes, requiring separate flood or earthquake insurance policies. Understanding these three elements is paramount to assessing the true cost and protection offered by your policy.
Common Exclusions in Homeowners Insurance Policies
Several common exclusions exist in most homeowners insurance policies. These exclusions often involve events considered high-risk or easily preventable. Knowing these beforehand allows you to take appropriate steps to mitigate risk or secure additional coverage.
| Exclusion | Description | Mitigation Strategies | Additional Coverage Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flood Damage | Damage caused by overflowing bodies of water, such as rivers or lakes. | Purchase flood insurance, elevate valuables, install flood barriers. | National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) or private flood insurance. |
| Earthquake Damage | Damage caused by seismic activity. | Reinforce your home’s structure, purchase earthquake insurance. | Earthquake insurance rider or separate policy. |
| Acts of War | Damage resulting from acts of war or terrorism. | This is generally not insurable. | N/A |
| Neglect or Intentional Damage | Damage caused by the homeowner’s negligence or intentional acts. | Maintain your property properly, be mindful of safety regulations. | N/A (coverage is typically excluded) |
Understanding Policy Terminology
Understanding key terms within your policy is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of your coverage. Familiarizing yourself with these terms will allow you to accurately assess your level of protection.
| Term | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Actual Cash Value (ACV) | The replacement cost of your property minus depreciation. | A five-year-old sofa with an original cost of $1000 and 20% annual depreciation would have an ACV of $600. |
| Replacement Cost | The cost to repair or replace your damaged property with new materials of like kind and quality, without considering depreciation. | Replacing the same $1000 sofa after five years would cost $1000 under replacement cost coverage. |
| Liability Coverage | Protection against financial responsibility for injuries or property damage caused to others on your property. | If someone slips and falls on your icy sidewalk and sues you, your liability coverage would help pay for their medical bills and legal fees. |
| Deductible | The amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage begins. | If your deductible is $1000 and you have $5000 in damages, you pay $1000 and the insurance company pays $4000. |
Impact of Home Improvements on Insurance Rates
Home improvements can significantly influence your homeowners insurance premiums. While some upgrades might increase your initial costs, many ultimately lead to lower rates over time by mitigating risks and demonstrating a commitment to property maintenance. Understanding this relationship can help you make informed decisions about home renovations and save money on your insurance.
Making improvements that reduce the likelihood of damage or theft can lead to substantial cost savings on your insurance premiums. Insurance companies recognize that homes with enhanced safety features and updated systems are less prone to certain types of claims. This translates to lower risk for the insurer, and consequently, lower premiums for you.
Security System Installation
Installing a monitored security system is a prime example of a home improvement that typically results in lower insurance rates. Many insurers offer discounts for homes equipped with burglar alarms, fire alarms, and security cameras. These systems deter potential intruders and provide faster response times in emergencies, leading to reduced property damage and loss. For instance, a homeowner with a monitored security system might receive a 5-10% discount on their annual premium, depending on the insurer and the specifics of the system. The savings can quickly offset the cost of installation over time.
Roofing and Plumbing Upgrades
Replacing an aging roof with new, high-quality materials is another improvement that can positively impact insurance rates. A well-maintained roof is less susceptible to damage from wind, hail, or snow, minimizing the risk of costly repairs or replacements. Similarly, upgrading outdated plumbing systems can reduce the risk of water damage, a common and expensive claim for homeowners insurance. Imagine a scenario where a homeowner replaces their old, leaky pipes with modern, PEX piping. This proactive measure could reduce their insurance premium by avoiding the potential for costly water damage claims in the future. The specific discount will depend on the insurer and the extent of the upgrades.
Impact of Negative Improvements
It’s important to note that not all home improvements lead to lower insurance premiums. Some modifications, particularly those that increase the value of your home significantly without addressing safety concerns, might result in higher premiums. For example, adding a large, expensive addition to your home might increase your insurance costs due to the higher replacement value. Similarly, installing a swimming pool, while enhancing the property’s value, often leads to increased premiums because of the inherent risk associated with pool accidents. The insurer will assess the increased liability associated with the new addition, which could lead to a higher premium. It’s always wise to discuss any major renovations with your insurance provider before starting the project.
Bundling Insurance Policies for Savings
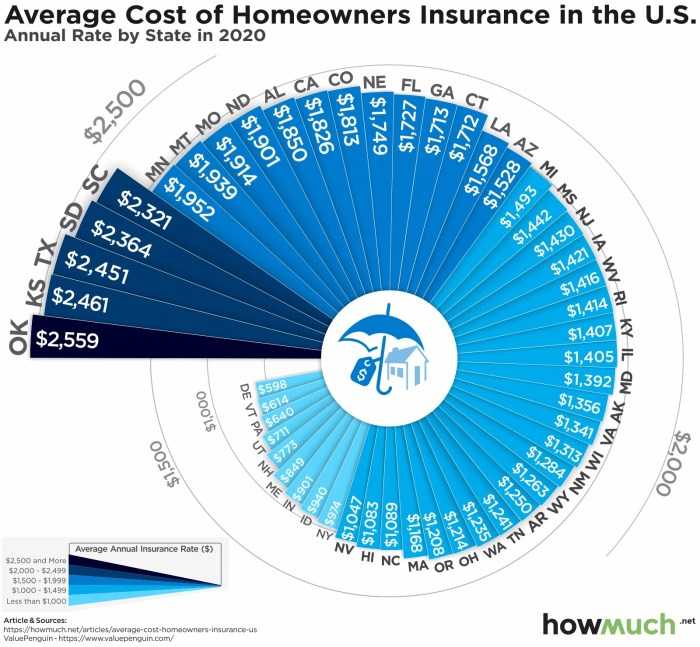
Bundling your homeowners insurance with other insurance policies, most commonly auto insurance, is a popular strategy for saving money. Insurance companies often offer discounts when you purchase multiple policies from them, recognizing the reduced risk and administrative costs associated with managing a single customer’s diverse insurance needs. This practice can lead to significant cost savings over time, making it a worthwhile consideration for many homeowners.
Many insurance companies offer discounts for bundling homeowners and auto insurance, and sometimes even additional policies like renters, umbrella, or life insurance. These discounts are typically expressed as a percentage reduction in the overall premium, but the exact amount varies based on several factors including your individual risk profile, the specific policies bundled, and the insurance company’s pricing structure. While the savings might seem modest on a single policy, the cumulative effect of combining several policies can lead to substantial cost reductions annually.
Bundling Benefits and Drawbacks
Bundling insurance policies presents several advantages. The most obvious benefit is the financial savings achieved through discounted premiums. This can free up a significant portion of your budget for other priorities. Beyond cost savings, bundling can also simplify your insurance management. Having all your policies with a single provider means dealing with only one company for billing, claims, and customer service, which streamlines the entire process. This consolidated approach simplifies paperwork, reduces potential confusion, and makes it easier to track your coverage.
However, there are potential drawbacks to consider. Bundling might limit your options when it comes to choosing insurers. Sticking with one company for all your insurance needs could mean missing out on better rates or coverage offered by specialized insurers in a particular area, such as those offering highly competitive rates for homeowners insurance in specific geographic locations. Additionally, while dealing with a single provider simplifies things, a poor customer service experience with that provider will affect all your bundled policies.
Examples of Bundling Savings
Let’s consider a hypothetical example. Suppose a homeowner pays $1,200 annually for homeowners insurance and $800 annually for auto insurance with separate providers. If they bundled these policies with a company offering a 15% discount on bundled policies, their combined annual premium would be reduced. The total premium without bundling is $2000. A 15% discount would amount to $300 ($2000 * 0.15), resulting in a total annual premium of $1700. This represents a savings of $300 per year.
Another example could involve a family with a homeowners policy, two auto insurance policies, and a life insurance policy. The cumulative savings from bundling all four policies could be substantially higher than the savings from just bundling homeowners and auto insurance, potentially amounting to hundreds of dollars in annual savings. The precise amount depends on the individual premiums and the discount offered by the insurer. It’s crucial to compare quotes from multiple insurers to find the best bundling deal tailored to your specific needs and risk profile.
The Role of Discounts in Lowering Premiums
Securing affordable homeowners insurance often hinges on understanding and leveraging available discounts. Insurance companies offer a range of discounts to incentivize responsible homeownership and risk mitigation. By taking advantage of these, homeowners can significantly reduce their annual premiums. This section will explore several common discount types and their eligibility criteria.
Many factors influence the specific discounts offered and the amount of savings they provide. These can vary by insurance company, state, and even individual policy details. It’s crucial to contact your insurer or a broker to determine your eligibility for specific discounts.
Common Homeowners Insurance Discounts
Understanding the various discounts available is key to minimizing your insurance costs. Taking proactive steps to improve your home’s security and maintain a positive insurance history can lead to substantial savings over time. Below is a list of five common discounts that many homeowners can qualify for.
- Multi-Policy Discount: Bundling your homeowners insurance with other policies, such as auto insurance, from the same company often results in a significant discount. This is because the insurer benefits from managing multiple policies for a single customer, streamlining administrative processes and reducing overall risk. Eligibility requires purchasing at least two qualifying policies from the same insurer. For example, a 10% discount on your homeowners insurance could be applied if you also have your car insurance with the same company.
- Loyalty Discount: Insurers frequently reward long-term policyholders with loyalty discounts. This reflects the reduced risk associated with established customers who have consistently maintained their policies over an extended period. The length of time required to qualify for a loyalty discount varies by insurer, but it typically ranges from three to five years of continuous coverage. A typical loyalty discount might be 5% after five years of continuous coverage with the same company.
- Safety Device Discount: Installing security devices, such as alarm systems, smoke detectors, and fire sprinklers, can significantly reduce the risk of property damage and theft. Many insurers offer discounts to homeowners who install and maintain these safety features. The specific discount and eligibility criteria vary depending on the type of device and the insurer’s requirements; for instance, a monitored alarm system might yield a larger discount than a basic smoke detector.
- Home Security System Discount: This discount is specifically targeted at homeowners who invest in professionally monitored security systems. The presence of a monitored system indicates a lower risk of burglary and other related claims, justifying the discount. To qualify, the system typically needs to be professionally installed and monitored by a reputable security company, with proof of monitoring provided to the insurer.
- Claims-Free Discount: Maintaining a clean claims history demonstrates responsible homeownership and a reduced likelihood of future claims. Insurers often reward this responsible behavior with discounts. The duration of the claims-free period required for eligibility varies by insurer. For example, a 15% discount might be offered after five years without filing any claims.
Conclusion
Finding the best homeowners insurance rates is a journey, not a destination. By diligently comparing quotes, understanding policy nuances, and leveraging available discounts, you can significantly reduce your premiums without compromising essential coverage. Remember that proactive steps, such as home improvements and bundling policies, can further enhance cost savings. Ultimately, securing the right insurance policy provides peace of mind, knowing your home is adequately protected against unforeseen circumstances.
Detailed FAQs
What is a deductible?
A deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in.
How often should I review my homeowners insurance policy?
It’s advisable to review your policy annually or whenever significant life changes occur (e.g., home renovations, additions to the family).
Can I get homeowners insurance if I have a poor credit score?
Yes, but a lower credit score will likely result in higher premiums. Some insurers specialize in working with individuals who have less-than-perfect credit.
What is the difference between replacement cost and actual cash value?
Replacement cost covers the full cost of repairing or replacing damaged property with new materials, while actual cash value considers depreciation.
What types of discounts are typically available?
Common discounts include multi-policy discounts (bundling home and auto), security system discounts, and loyalty discounts for long-term policy holders.