Securing your home with insurance is a crucial step in responsible homeownership, but navigating the complexities of premiums can feel overwhelming. The average price of home insurance varies significantly, influenced by a multitude of factors ranging from your location and home’s characteristics to your personal credit history and the level of coverage you choose. This guide unravels the mysteries behind home insurance costs, providing you with the knowledge to make informed decisions and find the best coverage at a price that suits your budget.
We’ll delve into the key elements that determine your premium, exploring how factors like location, home age, coverage type, and claims history all play a role. We’ll also examine geographical variations in insurance costs and offer practical strategies for securing affordable home insurance, including tips on comparing quotes and leveraging available discounts. By the end, you’ll have a clearer understanding of what influences the average price of home insurance and how to navigate the process effectively.
Factors Influencing Home Insurance Costs
Several interconnected factors determine the price of home insurance. Understanding these elements allows homeowners to make informed decisions about their coverage and potentially reduce their premiums. This section will explore the key factors influencing home insurance costs, providing examples and strategies for mitigation.
Location
Geographic location significantly impacts home insurance premiums. Areas prone to natural disasters, such as hurricanes, earthquakes, wildfires, or floods, command higher premiums due to the increased risk of damage. For instance, a home in a coastal region susceptible to hurricanes will generally cost more to insure than a similar home in a landlocked area with minimal risk of natural disasters. Furthermore, the crime rate in a neighborhood also plays a role; higher crime rates often translate to higher insurance costs due to the increased risk of theft or vandalism.
Home Age and Construction
Older homes, especially those lacking modern safety features like updated electrical systems or fire-resistant materials, tend to have higher insurance premiums than newer homes. This is because older homes are often considered to be at a greater risk of damage or loss. The type of construction also matters; homes built with fire-resistant materials, such as brick or concrete, may receive lower premiums compared to those constructed with wood framing. A well-maintained older home, however, might attract more favorable rates than a poorly maintained newer home.
Coverage Levels
The level of coverage selected directly influences the premium. Higher coverage limits for dwelling, personal property, liability, and other aspects naturally result in higher premiums. Conversely, choosing lower coverage limits will reduce the premium but also increases the financial risk to the homeowner in the event of a significant loss. It’s crucial to strike a balance between adequate protection and affordability. For example, opting for a higher liability limit protects against significant lawsuits, but this comes at a higher cost.
Credit Score and Claims History
Insurers often use credit scores as an indicator of risk. Individuals with good credit scores typically receive lower premiums than those with poor credit. This is because a good credit score suggests responsible financial behavior, implying a lower likelihood of filing fraudulent claims or failing to pay premiums. Similarly, a clean claims history (no or few claims filed in the past) results in lower premiums. Conversely, multiple claims filed in a short period can significantly increase premiums, reflecting a higher perceived risk to the insurer.
| Factor | Impact on Premium | Example | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Location | Higher premiums in high-risk areas | Coastal home in hurricane-prone zone vs. inland home | Consider moving to a lower-risk area (if possible), implement home security measures |
| Home Age and Construction | Older homes/homes with inferior construction = higher premiums | Older wood-framed home vs. newer brick home | Upgrade home safety features, maintain the home diligently, consider home improvements |
| Coverage Levels | Higher coverage = higher premiums | $500,000 dwelling coverage vs. $300,000 dwelling coverage | Carefully evaluate coverage needs, consider higher deductibles |
| Credit Score and Claims History | Good credit and clean claims history = lower premiums | Individual with excellent credit and no claims vs. individual with poor credit and multiple claims | Improve credit score, prevent future claims by taking preventative measures |
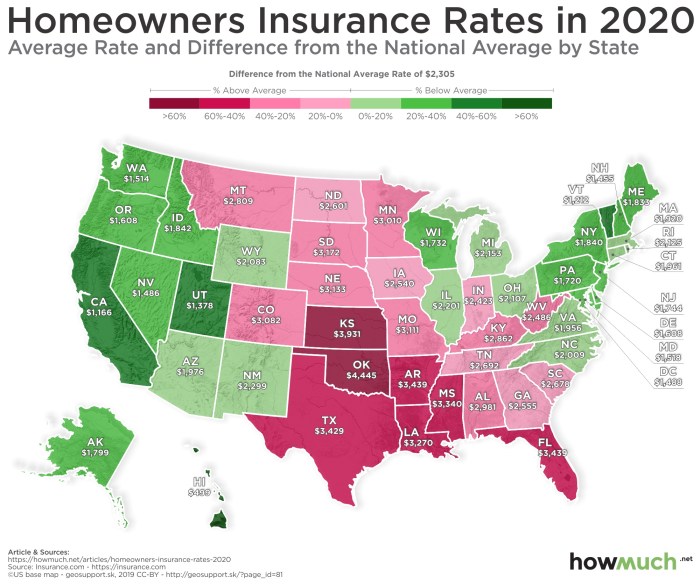
Average Home Insurance Costs by Location
Home insurance premiums vary significantly across the United States, influenced by a complex interplay of factors. Understanding these regional differences is crucial for homeowners seeking the best value and appropriate coverage. This section details average costs by location, highlighting contributing factors and the impact of geographical risks.
Geographical variations in home insurance costs are primarily driven by the likelihood and severity of natural disasters, the density of population, and the prevalence of crime. Areas prone to hurricanes, wildfires, earthquakes, or floods typically command higher premiums due to the increased risk to insurers. Conversely, areas with lower crime rates and a lower incidence of natural disasters often enjoy lower premiums.
Average Home Insurance Premiums by State/Region
The following table presents estimated average home insurance premiums for selected states and regions. Note that these are averages and individual premiums will vary based on specific factors such as the type of home, coverage level, and the homeowner’s claims history. The “Premium Range” reflects the typical spread observed within each region.
| State/Region | Average Premium | Premium Range | Contributing Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Florida | $2,000 | $1,500 – $3,000 | High hurricane risk, coastal properties, frequent storm damage claims. |
| California | $1,800 | $1,200 – $2,500 | Wildfire risk (particularly in certain areas), earthquake risk, high property values. |
| Texas | $1,500 | $1,000 – $2,200 | Hailstorms, tornadoes, high property values in some areas. |
| Midwest (e.g., Iowa, Nebraska) | $1,000 | $700 – $1,400 | Lower risk of major natural disasters, lower property values compared to coastal areas. |
| Northeast (e.g., Maine, Vermont) | $1,200 | $800 – $1,800 | Winter storms, potential for flooding, moderate property values. |
Natural Disaster Risk and Home Insurance Pricing
The impact of natural disaster risk on home insurance pricing is significant and directly proportional to the probability and potential severity of the event. For example, coastal areas in Florida face substantially higher premiums due to the frequent threat of hurricanes. Similarly, regions of California prone to wildfires see premiums inflated to reflect the increased risk of property damage and loss.
Insurers use sophisticated models to assess risk, factoring in historical data on natural disaster frequency, intensity, and the vulnerability of individual properties. Homes located in high-risk zones, such as floodplains or areas with a history of wildfires, will generally incur higher premiums than those in lower-risk areas. This reflects the increased likelihood of claims and the potentially substantial payouts insurers might face in the event of a disaster.
For instance, a home located in a designated flood zone in Florida might see its premium significantly increased compared to a similar home located inland. Similarly, a home built with fire-resistant materials in a wildfire-prone area of California may still face higher premiums than a comparable home in a lower-risk zone, although the premium increase may be less substantial.
Finding Affordable Home Insurance
Securing affordable home insurance requires a proactive approach, involving careful planning and strategic decision-making. By understanding the factors influencing costs and employing effective strategies, homeowners can significantly reduce their premiums without compromising necessary coverage. This section Artikels key steps to achieve lower insurance costs.
Strategies for Reducing Home Insurance Costs
Several methods can help lower your home insurance premiums. Implementing these strategies can lead to substantial savings over the policy’s lifespan.
Home Security Upgrades
Investing in home security enhancements can significantly reduce your insurance costs. Many insurers offer discounts for features like security systems with monitoring, smoke detectors, and deadbolt locks. These measures demonstrate a lower risk profile to the insurer, resulting in reduced premiums. For example, installing a monitored alarm system could earn you a 5-10% discount, while fire-resistant roofing materials might yield a similar or even greater reduction. The specific discount varies depending on the insurer and the level of security implemented.
Improving Your Credit Score
Your credit score is a significant factor in determining your insurance premiums. A higher credit score often correlates with lower risk, leading to lower premiums. Improving your credit score through responsible financial management can translate to substantial savings on your home insurance. This is because insurers view individuals with good credit as more reliable and less likely to file fraudulent claims.
Bundling Insurance Policies
Many insurance companies offer discounts for bundling multiple policies, such as home and auto insurance. This bundling strategy simplifies management and often results in a combined discount, offering significant savings compared to purchasing each policy separately. For instance, bundling your home and auto insurance with the same provider could reduce your overall premium by 10-15%, depending on the insurer and the specific policies.
Discounts Offered by Insurers
Insurers frequently offer a range of discounts to attract and retain customers. Understanding and taking advantage of these discounts is crucial for securing affordable coverage.
Common Home Insurance Discounts
- Multi-policy discounts: As mentioned above, bundling home and auto insurance often results in a significant discount.
- Security system discounts: Installing and maintaining a monitored security system typically leads to a discount.
- Claim-free discounts: Maintaining a clean claims history often rewards policyholders with reduced premiums.
- Loyalty discounts: Long-term policyholders may qualify for discounts for their continued business.
- Home safety feature discounts: Features such as smoke detectors, fire extinguishers, and upgraded roofing materials can lead to lower premiums.
Comparing Quotes from Multiple Insurers
Obtaining quotes from multiple insurers is essential for finding the most affordable home insurance. This comparative approach ensures you secure the best possible coverage at the most competitive price.
The Quote Comparison Process
To effectively compare quotes, gather information about your property, including its value, location, and features. Then, contact several insurers, providing them with consistent information for accurate comparisons. Carefully review each quote, paying close attention to coverage limits, deductibles, and exclusions. Don’t solely focus on the price; ensure the coverage adequately protects your home and belongings. This process helps to identify the best balance between cost and coverage.
Understanding Policy Details Before Purchasing
Thoroughly understanding your policy’s details before purchasing is crucial to avoid unexpected costs or insufficient coverage. This involves careful review of the policy document and clarification of any ambiguities with the insurer.
Policy Details to Review
- Coverage limits: Ensure the coverage limits are sufficient to rebuild your home and replace your belongings in case of a covered loss.
- Deductibles: Understand your deductible amount, as this is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in.
- Exclusions: Review the policy exclusions carefully to understand what events or damages are not covered.
- Premium payment options: Explore different payment options to determine the most convenient and cost-effective method for you.
Summary

Understanding the average price of home insurance is not merely about finding the cheapest policy; it’s about finding the right balance between cost and comprehensive protection. By carefully considering the factors influencing premiums, comparing quotes from multiple insurers, and leveraging available discounts, you can secure a policy that offers peace of mind without breaking the bank. Remember, proactive planning and informed decision-making are key to securing affordable and adequate home insurance coverage.
Key Questions Answered
What is the difference between actual cash value (ACV) and replacement cost coverage?
ACV coverage pays for the current market value of your damaged property, minus depreciation. Replacement cost coverage pays for the cost to replace your damaged property with new, similar items, regardless of depreciation.
How often can I expect my home insurance premiums to change?
Premiums can change annually, and sometimes more frequently, depending on your insurer’s policies and any changes in your risk profile (e.g., claims, improvements to your home).
Can I bundle my home and auto insurance for a discount?
Yes, many insurers offer discounts for bundling home and auto insurance policies. This is a common strategy to save money.
What should I do if I’m denied a home insurance claim?
Review your policy carefully, gather all relevant documentation, and contact your insurer to discuss the denial. If you’re unsatisfied, you may wish to contact your state’s insurance commissioner’s office.