Securing your home is a significant financial investment, and understanding the nuances of home insurance is crucial. This guide delves into the complexities of average home insurance rates, exploring the factors that influence premiums and offering strategies to secure the best coverage at the most competitive price. From location-based risk assessments to the impact of personal choices, we’ll unravel the key elements shaping your insurance costs.
Navigating the world of home insurance can feel overwhelming, with varying policy types, coverage options, and a multitude of factors impacting your premiums. This guide aims to demystify the process, providing clear explanations and practical advice to help you make informed decisions and secure the best possible protection for your home.
Factors Influencing Average Home Insurance Rates
Understanding the factors that influence your home insurance premiums is crucial for securing adequate coverage at a manageable cost. Several key elements contribute to the final price you pay, and being aware of these can help you make informed decisions about your policy.
Location’s Impact on Home Insurance Costs
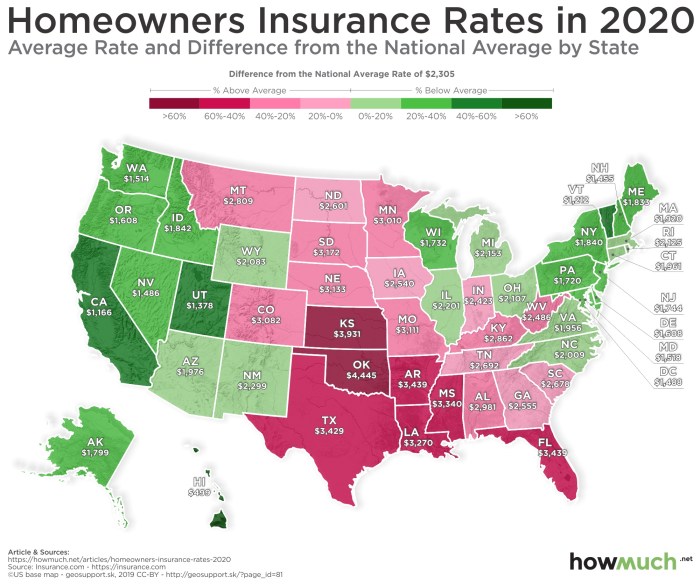
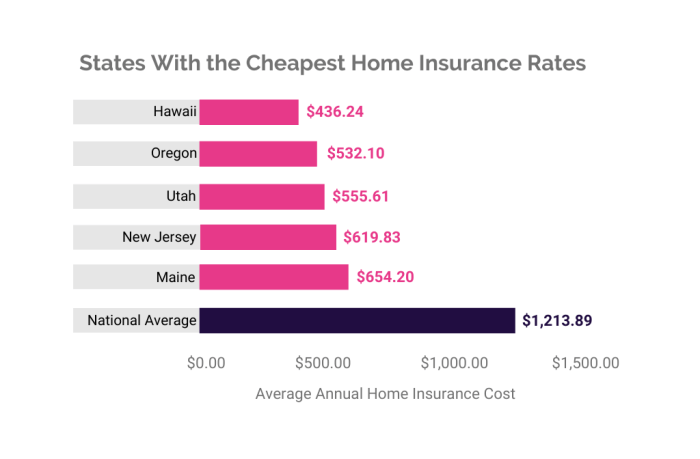
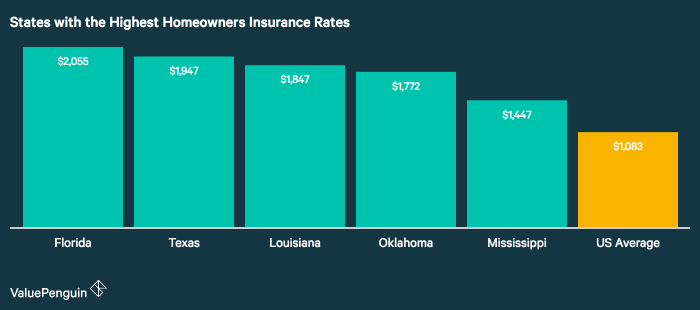
Geographic location significantly impacts home insurance rates due to varying risks of natural disasters, crime rates, and other factors. Coastal areas, for instance, are often subject to higher premiums due to the increased risk of hurricanes, floods, and storm surges. Conversely, areas with lower crime rates and minimal natural disaster risks tend to have lower premiums. For example, a home in hurricane-prone Florida will typically command a higher premium than a similar home in a less-vulnerable state like Iowa. The following table illustrates average annual premiums for a standard homeowner’s insurance policy across several states:
| State | Average Annual Premium | State | Average Annual Premium |
|---|---|---|---|
| Florida | $2,000 | Iowa | $800 |
| California | $1,500 | Nebraska | $750 |
| Texas | $1,200 | Kansas | $850 |
| Louisiana | $1,800 | Ohio | $1000 |
*Note: These figures are illustrative examples and may vary based on specific factors.*
Home Features and Premium Adjustments
The characteristics of your home play a significant role in determining your insurance premium. Features such as age, size, construction materials, and security systems all influence the perceived risk and, consequently, the cost of insurance. Older homes, for example, may require more extensive repairs and thus carry higher premiums than newer homes. Similarly, larger homes typically cost more to insure. Security systems, on the other hand, can lead to premium discounts as they deter burglaries and reduce the insurer’s risk.
| Home Feature | Premium Adjustment |
|---|---|
| Security System (Alarm & Monitoring) | -10% to -20% |
| Fire Sprinkler System | -5% to -15% |
| Impact-Resistant Windows | -5% to -10% |
| Home Age (Over 50 years old) | +5% to +15% |
| Home Size (Over 3000 sq ft) | +10% to +20% |
*Note: These are sample adjustments and vary widely based on insurer and specific circumstances.*
Homeowner’s Insurance Coverage Levels and Deductibles
The level of coverage you choose directly impacts your premium. Higher coverage limits mean greater protection in case of damage or loss but also result in higher premiums. Conversely, choosing a higher deductible (the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in) will lower your premium, but you will have to pay more in the event of a claim. For example, a $250,000 coverage policy with a $1,000 deductible will typically have a lower premium than a $500,000 policy with a $500 deductible.
Credit Score and Claims History
Your credit score and claims history are significant factors influencing your home insurance rates. Insurers often view a good credit score as an indicator of responsible financial behavior, leading to lower premiums. Conversely, a poor credit score may result in higher premiums. Similarly, a history of frequent claims can increase your premiums as it suggests a higher risk to the insurer. For example, an individual with an excellent credit score and no claims in the past five years might receive a significantly lower rate compared to someone with a poor credit score and multiple claims.
Understanding Different Types of Home Insurance Policies
Choosing the right home insurance policy is crucial for protecting your most valuable asset. Different policies offer varying levels of coverage and cost, making it essential to understand the nuances before making a decision. This section will explore common policy types, their features, and the associated costs.
Comparison of Home Insurance Policy Types
The most common types of homeowner’s insurance policies are HO-3, HO-4, and HO-6. Understanding their differences is key to selecting the appropriate coverage for your specific needs and situation.
- HO-3 (Special Form): This is the most common type of homeowner’s insurance. It provides open-peril coverage for your dwelling and other structures (like a detached garage), meaning it covers damage from almost any cause except those specifically excluded in the policy. Personal property is covered on a named-peril basis, meaning it only covers damage from specific listed events (e.g., fire, theft, wind). HO-3 policies typically offer comprehensive coverage at a moderate cost.
- HO-4 (Renters Insurance): Designed for renters, this policy covers personal property against loss or damage from covered perils. It also provides liability coverage, protecting you if someone is injured on your rented property. HO-4 policies are generally less expensive than homeowner’s policies because they don’t cover the structure itself.
- HO-6 (Condominium Insurance): This policy is specifically for condominium owners. It covers the interior of the condo unit and personal property, similar to an HO-3 policy, but the building’s exterior and common areas are typically covered by the condominium association’s master policy. The cost of an HO-6 policy is usually lower than an HO-3 policy because it covers less.
Common Exclusions and Limitations in Home Insurance Policies
Standard home insurance policies typically exclude coverage for certain events and circumstances. It’s vital to be aware of these limitations to avoid unexpected financial burdens.
- Acts of God: While some policies may cover certain aspects of natural disasters, widespread events like earthquakes and floods are often excluded unless you purchase specific endorsements.
- Neglect or Intentional Damage: Damage resulting from your own negligence or intentional acts is generally not covered. For example, failing to maintain your property adequately or deliberately damaging it.
- Gradual Damage: Damage caused by gradual wear and tear, such as foundation settling or rust, is typically not covered.
- Certain Pests: Damage caused by insects or rodents is often excluded unless it results from a covered peril (e.g., a fire that attracts termites).
For example, if a tree falls on your house due to a severe storm, your HO-3 policy would likely cover the damage. However, if the tree falls due to neglect (e.g., you failed to trim overgrown branches), the damage may not be covered. Similarly, damage from a slow, gradual water leak might not be covered.
Importance of Additional Coverage Options
While standard policies offer essential protection, additional coverage options can provide crucial protection against specific risks.
- Flood Insurance: Flood damage is frequently excluded from standard homeowner’s insurance. Separate flood insurance is often required, particularly in flood-prone areas. The cost varies based on location and risk assessment. The benefit is protection against potentially devastating flood damage.
- Earthquake Insurance: Similar to flood insurance, earthquake coverage is typically not included in standard policies. It’s a valuable addition in seismically active regions, but it can be expensive. The benefit is clear in preventing financial ruin from an earthquake.
- Liability Coverage: This protects you against financial responsibility if someone is injured on your property or if you accidentally damage someone else’s property. Increased liability limits offer enhanced protection but at a higher cost. The benefit is crucial in mitigating potentially significant legal and financial liabilities.
For instance, a guest tripping and injuring themselves on your property could lead to significant medical expenses and legal fees. Adequate liability coverage would help protect your finances in such a scenario.
Obtaining Multiple Quotes and Comparing Insurance Providers
Finding the best home insurance deal involves comparing quotes from multiple insurers.
- Identify your needs: Determine the level of coverage you require, considering the value of your home, personal belongings, and desired liability protection.
- Gather information: Collect information about your property, including its age, square footage, and any relevant upgrades.
- Use online comparison tools: Several websites allow you to compare quotes from multiple insurers simultaneously.
- Contact insurers directly: Supplement online quotes by contacting insurers directly to discuss specific needs and ask clarifying questions.
- Compare policies carefully: Analyze coverage details, deductibles, and premiums before making a decision. Don’t solely focus on the price; ensure the coverage meets your needs.
By following these steps, you can obtain a comprehensive comparison of home insurance options and choose the policy that best balances cost and coverage.
Final Review
Ultimately, understanding average home insurance rates requires a multifaceted approach. By carefully considering the factors influencing premiums, comparing different policy types and providers, and implementing cost-saving strategies, homeowners can secure adequate coverage while managing their expenses effectively. Remember that regular review and proactive engagement with your insurer are key to maintaining optimal protection and value for your investment.
Helpful Answers
What is the average cost of home insurance?
The average cost varies significantly based on location, home value, coverage, and other factors. There’s no single “average” number.
How often should I review my home insurance policy?
At least annually, or whenever there are significant changes to your home, possessions, or risk profile (e.g., renovations, additions, increased valuables).
Can I get home insurance without a credit check?
Some insurers offer policies without credit checks, but these may be more expensive. Your options will depend on your location and the insurer.
What happens if I file a claim and my rates increase?
Filing a claim can affect your rates, but the extent depends on the claim’s nature and your insurer’s policy. Some insurers offer claim forgiveness programs.
What are some common exclusions in home insurance policies?
Common exclusions include flood damage, earthquake damage, and intentional acts. Review your policy for specific exclusions.