Securing your home is a significant investment, and understanding the associated costs is crucial. This guide delves into the complexities of average home insurance costs, exploring the numerous factors that influence premiums and providing actionable strategies for minimizing expenses. From location and home features to credit scores and policy choices, we’ll unravel the intricacies of this essential financial aspect of homeownership.
Navigating the world of home insurance can feel overwhelming, with a multitude of providers, policies, and coverage options. This comprehensive resource aims to demystify the process, empowering you to make informed decisions and secure the best possible protection for your most valuable asset.
Understanding Insurance Quotes and Policies
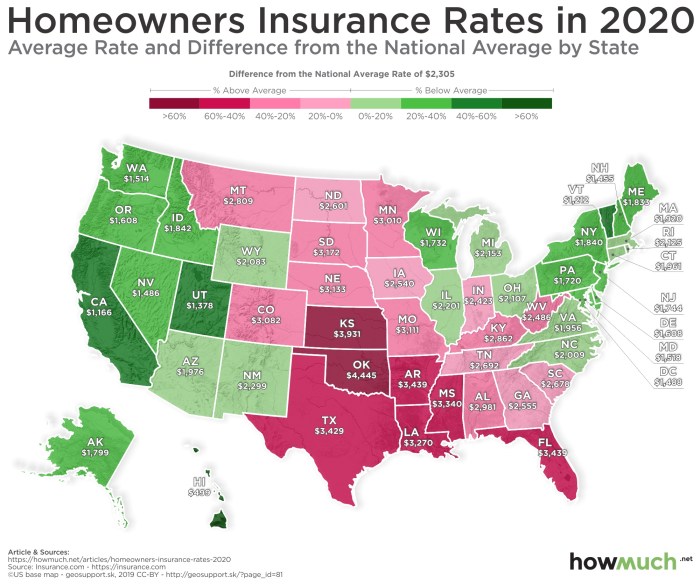
Securing adequate home insurance involves carefully reviewing quotes and understanding your policy’s details. This section will clarify the components of a typical quote, the process of obtaining multiple quotes, common policy exclusions, and the claims process. Understanding these aspects empowers you to make informed decisions and secure the best coverage for your needs.
Home Insurance Quote Components
A home insurance quote typically includes several key components. These components contribute to the overall premium and reflect the insurer’s assessment of risk. A comprehensive understanding of these elements is crucial for comparison shopping.
- Coverage Amounts: This specifies the maximum amount the insurer will pay for different types of losses, such as dwelling coverage (damage to the structure), personal property coverage (belongings inside the home), liability coverage (legal responsibility for injuries or damages to others), and additional living expenses (temporary housing if your home is uninhabitable).
- Deductible: This is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. Higher deductibles generally result in lower premiums.
- Premium: This is the amount you pay regularly (monthly, annually, or semi-annually) for your insurance coverage.
- Policy Period: This defines the duration of your insurance coverage, usually one year.
- Discounts: Many insurers offer discounts for various factors, such as security systems, fire alarms, bundling policies (home and auto), or being a long-term customer. These discounts can significantly impact your overall premium.
Obtaining Multiple Insurance Quotes
Comparing quotes from multiple insurers is essential to finding the best coverage at the most competitive price. A systematic approach ensures you thoroughly explore your options.
- Identify Potential Insurers: Research various insurance companies operating in your area. Consider both large national insurers and smaller regional companies.
- Gather Necessary Information: Before contacting insurers, gather information about your home, including its age, square footage, construction materials, and any recent renovations. You will also need details about your personal property.
- Request Quotes Online: Many insurers offer online quote tools that allow you to quickly receive estimates. Be sure to provide accurate information.
- Contact Insurers Directly: For a more personalized approach, contact insurers directly by phone or email. This allows you to ask specific questions and clarify any uncertainties.
- Compare Quotes Carefully: Once you receive quotes, compare them side-by-side, paying close attention to coverage amounts, deductibles, premiums, and any included discounts. Don’t solely focus on the lowest premium; consider the overall value and coverage offered.
Common Policy Exclusions and Limitations
Understanding policy exclusions and limitations is vital. These provisions Artikel situations where your insurance coverage may not apply.
- Acts of God: Coverage for damage caused by events like earthquakes or floods often requires separate policies or endorsements, depending on your location and insurer.
- Intentional Acts: Damage resulting from intentional acts by the policyholder is typically excluded.
- Neglect: Failure to maintain your property properly (e.g., ignoring necessary repairs) might affect coverage for resulting damages.
- Specific Perils: Certain perils may be excluded or require additional coverage. For example, some policies may exclude damage from specific types of pests or mold.
- Wear and Tear: Normal wear and tear on your home or belongings is generally not covered.
Filing a Claim and Claim Payouts
The claims process involves several steps. The speed and outcome of your claim depend on various factors.
The following flowchart illustrates the claim process:
[Flowchart Description:] The flowchart begins with “Incident Occurs.” This leads to “Report the Claim to Your Insurer (Phone or Online).” Next, the process branches into two paths: “Investigation and Assessment of Damages” and “Claim Denied (Reasons Provided).” The “Investigation and Assessment” path leads to “Claim Approved” which then branches into “Payment Received” and “Disputes/Appeals.” The “Claim Denied” path also leads to “Disputes/Appeals.” The “Disputes/Appeals” path leads to a final resolution.
Factors influencing claim payouts include the extent of the damage, the policy’s coverage limits, the deductible, and the accuracy and completeness of the information provided during the claims process. For example, a fire causing significant structural damage will result in a larger payout than minor water damage. Similarly, providing thorough documentation and cooperating fully with the insurer’s investigation will increase the chances of a smooth and timely claim settlement.
Summary
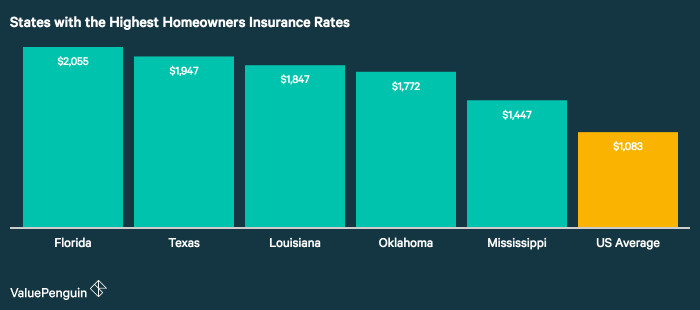
Ultimately, understanding your average home insurance cost requires a nuanced approach, considering a variety of interconnected factors. By carefully weighing the impact of location, home characteristics, credit score, policy choices, and proactive cost-saving measures, homeowners can secure adequate coverage while optimizing their premiums. This guide serves as a starting point for a thorough exploration of this crucial aspect of homeownership, enabling informed decisions and peace of mind.
FAQs
What is the difference between actual cash value and replacement cost coverage?
Actual cash value (ACV) covers the replacement cost minus depreciation, while replacement cost coverage pays the full cost of replacing damaged property regardless of depreciation.
How often can I expect my home insurance premiums to change?
Premiums are typically reviewed annually, and adjustments may occur based on factors like claims history, changes in coverage, or market fluctuations.
Can I get home insurance if I have a poor credit score?
Yes, but a poor credit score will likely result in higher premiums. Consider improving your credit score to access more favorable rates.
What happens if I need to file a claim during a natural disaster?
Contact your insurance provider immediately to report the damage. Follow their instructions regarding documentation and the claims process. Be prepared for potential delays due to high demand during widespread disasters.