Securing your home with adequate insurance is a crucial financial decision. Understanding the average cost of house insurance, however, can feel like navigating a maze. Numerous factors influence premiums, from your location’s risk profile to the specifics of your home and your personal credit history. This guide unravels the complexities, providing clarity on how to determine the right coverage at a price that fits your budget.
We’ll explore the various elements that contribute to the final cost, examining different policy types, comparing quotes from multiple providers, and offering strategies for securing the best possible rates. Ultimately, our aim is to empower you to make informed decisions about protecting one of your most valuable assets.
Factors Influencing House Insurance Costs
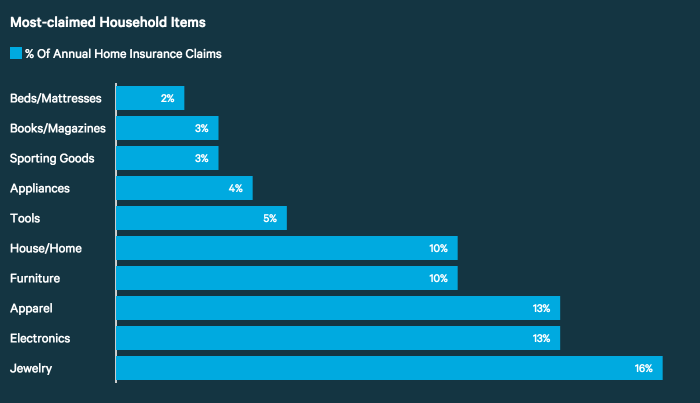
Several key factors significantly impact the cost of home insurance premiums. Understanding these factors can help homeowners make informed decisions to potentially lower their insurance expenses. This section will detail the influence of location, property condition, coverage levels, credit score, and other relevant aspects on your insurance premiums.
Location’s Impact on Home Insurance Premiums
The geographic location of your home is a primary determinant of your insurance costs. Insurance companies assess risk based on factors like the frequency of natural disasters (hurricanes, earthquakes, wildfires), crime rates, and the proximity to fire hydrants and emergency services. High-risk areas, such as coastal regions prone to hurricanes or areas with high wildfire risk (e.g., parts of California), will typically command higher premiums due to the increased likelihood of claims. Conversely, low-risk areas, such as those in the interior of the country with low crime rates and minimal natural disaster threats (e.g., certain parts of the Midwest), usually have lower premiums. For example, a home in a coastal town in Florida might see significantly higher premiums than a similar home in a rural area of Nebraska.
Age and Condition of the House and Their Effect on Insurance Costs
The age and condition of your house directly influence insurance costs. Older homes, particularly those lacking modern safety features or with outdated plumbing and electrical systems, are generally considered higher risk. The likelihood of needing repairs or experiencing damage increases with age. Conversely, newer homes, especially those built to modern building codes, often qualify for lower premiums. Specific repairs that can lead to lower premiums include upgrading to a newer, more efficient HVAC system, replacing an outdated electrical panel, installing updated plumbing, and reinforcing the roof. For instance, replacing a failing roof with impact-resistant shingles can substantially reduce your premium because it mitigates the risk of damage from hail or strong winds.
Coverage Levels and Their Influence on Premiums
The level of coverage you choose significantly impacts your insurance cost. Higher coverage limits for dwelling, liability, and other aspects result in higher premiums. For example, selecting a dwelling coverage limit that accurately reflects your home’s replacement cost will protect you in case of total loss, but will also result in a higher premium compared to underinsuring your property. Similarly, higher liability coverage protects you against significant lawsuits, but it will also cost more. Carefully evaluating your needs and choosing appropriate coverage levels is crucial to balance protection and affordability. Consider comparing premiums for different coverage options to find the best balance for your circumstances. A policy with a $500,000 liability limit will typically cost more than one with a $300,000 limit.
Credit Score’s Role in Determining Insurance Rates
Your credit score plays a significant role in determining your insurance rates. Insurance companies often use credit scores as an indicator of risk. A higher credit score generally suggests a lower risk profile, leading to lower premiums. Conversely, a lower credit score might indicate a higher risk and therefore higher premiums. This is because individuals with good credit are statistically less likely to file claims. Improving your credit score can be a tangible way to reduce your insurance costs over time. For example, a homeowner with an excellent credit score (750 or above) may qualify for significant discounts compared to someone with a poor credit score (below 600).
Other Factors Influencing House Insurance Costs
The following table summarizes other factors that can affect your home insurance costs:
| Factor | Impact on Cost | Example | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Security System | Lower premiums | Monitored alarm system | Install a monitored security system |
| Building Materials | Lower premiums for fire-resistant materials | Brick or concrete construction | Choose fire-resistant materials during construction or renovation |
| Home Maintenance | Lower premiums for well-maintained homes | Regular roof inspections, timely repairs | Regularly inspect and maintain your home |
| Claims History | Higher premiums for frequent claims | Multiple claims in the past few years | Maintain a good claims history by preventing damage and addressing issues promptly |
Types of Home Insurance and Their Costs
Choosing the right home insurance policy can significantly impact your financial well-being. Understanding the different types of policies and their associated costs is crucial for making an informed decision that best suits your needs and budget. This section will explore the common types of homeowner’s insurance, highlighting their coverage differences and typical cost ranges.
Home insurance policies are categorized based on the type of property and the level of coverage provided. The most common types are HO-3, HO-4, and HO-6, each designed for specific situations and offering varying degrees of protection. The premium you pay reflects the level of risk the insurer assumes, with broader coverage generally resulting in higher premiums.
HO-3, HO-4, and HO-6 Policy Comparisons
The cost of home insurance varies greatly depending on several factors, including location, property value, coverage limits, and the specific insurer. However, we can provide a general overview of the cost ranges and key differences among the three most prevalent types of homeowner’s insurance policies.
- HO-3 (Special Form): This is the most common type of homeowner’s insurance, offering broad coverage for damage to your home and personal belongings. It covers perils (causes of loss) specifically listed, as well as all other risks of direct physical loss, unless specifically excluded. Typical annual costs range from $600 to $1800, but this can vary widely based on location and coverage limits. For example, a homeowner in a high-risk hurricane zone will pay significantly more than someone in a low-risk area with the same coverage limits.
- HO-4 (Contents Broad Form): This policy is designed for renters and covers their personal belongings against loss or damage. It does not cover the structure itself. Because it covers fewer risks, premiums are generally lower than HO-3 policies, typically ranging from $200 to $600 annually. A renter in a large apartment with valuable possessions would likely pay more than someone with a smaller apartment and fewer belongings.
- HO-6 (Condominium Owner’s Coverage): This policy is tailored for condominium owners and covers their personal belongings and any improvements or alterations made to their unit. It typically does not cover the building’s structure itself, as that is usually covered by the condominium association’s master policy. The cost typically falls between HO-4 and HO-3, often ranging from $300 to $1200 annually, depending on the value of personal belongings and improvements. A condo owner with extensive renovations will pay more than one with a standard unit.
Coverage Provided and Premium Impact
The coverage offered by each policy directly influences the premium. HO-3 policies, offering the broadest coverage, generally command the highest premiums. Conversely, HO-4 policies, focusing solely on personal belongings, tend to have lower premiums. HO-6 policies fall somewhere in between, reflecting the balance of coverage they provide. For instance, additional coverage options, such as earthquake or flood insurance (often purchased separately), will increase the overall premium regardless of the base policy type.
Cost-Effectiveness Comparisons
The most cost-effective policy depends entirely on individual circumstances. For homeowners, an HO-3 policy is usually the most comprehensive and provides the best protection, although it comes with a higher premium. Renters, however, find HO-4 policies sufficient and more affordable. Condominium owners benefit from the tailored coverage of an HO-6 policy, balancing cost and coverage needs. For example, a young renter with minimal possessions might find an HO-4 policy perfectly adequate and cost-effective, while a homeowner with a valuable property in a high-risk area will likely prioritize the comprehensive coverage of an HO-3 policy despite the higher cost.
Obtaining Quotes and Comparing Insurance Providers
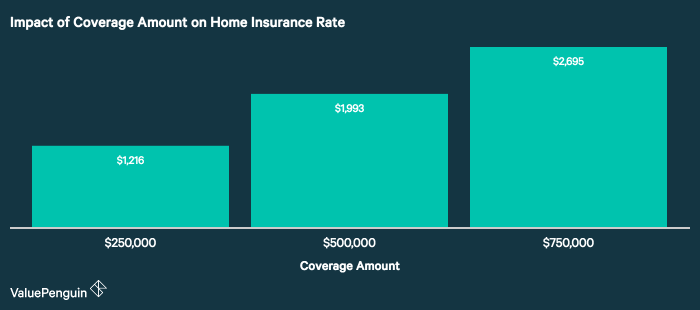
Securing the best home insurance requires a proactive approach to obtaining and comparing quotes from various providers. This process ensures you find a policy that offers the right balance of coverage and cost. Failing to compare quotes could result in overpaying for inadequate protection.
Obtaining Accurate Insurance Quotes: A Step-by-Step Guide
Gathering Accurate Information for Quotes
Before contacting insurers, gather all necessary information about your property. This includes your address, square footage, year built, type of construction (e.g., brick, wood), any security features (e.g., alarm system), and details about your coverage needs. Accurate information is crucial for receiving accurate quotes; inaccurate information can lead to discrepancies later.
Contacting Multiple Insurance Providers
Contact at least three to five different insurance providers. You can do this online through their websites, by phone, or through an independent insurance agent. Be sure to provide consistent information to each provider to allow for a fair comparison. Using online comparison tools can streamline this process, but remember to verify the information with the individual providers.
Requesting Specific Coverage Options
Clearly state your desired coverage levels for various perils, such as fire, theft, and liability. Don’t hesitate to ask questions about policy details and exclusions. Understanding what’s covered and what isn’t is crucial for making an informed decision. For example, you might want to specify flood or earthquake coverage if you live in a high-risk area.
Comparing Quotes from Multiple Insurance Companies
Comparing quotes from multiple companies is essential to finding the best value for your money. Different insurers use different rating models and offer varying coverage options at different price points. Simply choosing the cheapest option without considering the coverage could leave you underinsured.
Identifying and Avoiding Hidden Fees
Carefully review each quote for hidden fees or surcharges. These can include fees for processing payments, administrative charges, or additional charges for specific coverage options. Ask clarifying questions if anything is unclear. Look for a detailed breakdown of all costs associated with the policy, including any deductibles.
Factors to Consider Beyond Price
Choosing a home insurance provider involves more than just the price. Several other factors significantly influence the overall value of the policy.
Provider Comparison Table
| Provider | Cost (Annual Premium) | Coverage Highlights | Customer Service Rating (1-5 stars) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Company A | $1,200 | $250,000 dwelling coverage, $100,000 liability, standard deductibles | ★★★★☆ |
| Company B | $1,000 | $200,000 dwelling coverage, $50,000 liability, higher deductibles | ★★★☆☆ |
| Company C | $1,350 | $300,000 dwelling coverage, $100,000 liability, low deductibles, additional coverage for specific perils | ★★★★★ |
Understanding Policy Deductibles and Premiums
Home insurance premiums and deductibles are intrinsically linked; understanding their relationship is crucial for securing cost-effective coverage. Essentially, your deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in, while your premium is the regular payment you make to maintain your policy.
The inverse relationship between deductibles and premiums is straightforward: a higher deductible typically results in a lower premium, and vice-versa. This is because a higher deductible signifies a lower risk for the insurance company; they’re less likely to have to pay out a claim, so they can offer a lower premium. Conversely, a lower deductible means a higher likelihood of a claim, leading to a higher premium to offset the increased risk.
Deductible Types and Their Impact
Different types of deductibles exist, affecting how your out-of-pocket expenses are calculated. Understanding these variations is vital for making informed decisions.
A common type is the per-occurrence deductible. This applies separately to each incident covered by your policy. For example, if you have a $1,000 per-occurrence deductible and experience two separate incidents of damage, each requiring $2,000 in repairs, you would pay $2,000 out-of-pocket ($1,000 for each incident), and the insurance would cover the remaining $2,000.
In contrast, an aggregate deductible applies a single deductible amount to all claims within a specific policy period (usually a year). Using the same example, with a $1,000 aggregate deductible, you would only pay $1,000 out-of-pocket for both incidents combined, regardless of how many separate events caused the damage. The insurance would then cover the remaining $3,000.
Choosing a Deductible: Balancing Cost and Protection
Selecting the right deductible involves carefully weighing the potential cost savings of a higher deductible against your ability to absorb unexpected expenses. Consider your financial situation, emergency fund, and risk tolerance.
A higher deductible significantly lowers your premium, offering considerable savings over time. However, it also increases your financial vulnerability in the event of a claim. For example, a homeowner with a substantial emergency fund might comfortably choose a $5,000 deductible, knowing they can cover that amount without undue hardship. Conversely, someone with limited savings might opt for a lower deductible, such as $1,000, to minimize their out-of-pocket expenses, even if it means a higher premium.
Ultimately, the optimal deductible is a personal decision based on individual circumstances and risk assessment. It’s wise to explore different scenarios and compare the total cost (premium plus potential out-of-pocket expenses) to determine the best balance between cost savings and financial protection. Consulting with an insurance professional can provide valuable guidance in this process.
Saving Money on Home Insurance

Reducing your home insurance premiums can significantly impact your household budget. Several strategies can help lower your costs without compromising coverage. By understanding these options and implementing appropriate measures, you can save money while maintaining adequate protection for your home.
There are numerous ways to potentially reduce your home insurance premiums. Many of these involve making improvements to your property, adopting safer practices, or leveraging discounts offered by your insurer. Others involve strategic choices regarding your insurance policy itself.
Ways to Lower Home Insurance Premiums
Several actions can contribute to lower insurance premiums. These range from straightforward adjustments to more involved home improvements. Implementing even a few of these strategies can lead to noticeable savings over time.
- Improve your credit score: Insurance companies often consider credit history when determining premiums. A higher credit score generally translates to lower rates.
- Increase your deductible: Opting for a higher deductible means you’ll pay more out-of-pocket in the event of a claim, but it can significantly lower your premium. Carefully weigh the risk versus reward based on your financial situation.
- Bundle home and auto insurance: Many insurers offer discounts when you bundle your home and auto insurance policies. This is often a substantial savings opportunity.
- Install security systems: Security systems, including alarms, surveillance cameras, and motion detectors, can deter burglars and demonstrate to your insurer a lower risk profile, resulting in reduced premiums. Some companies even offer discounts for specific types of security systems.
- Make home improvements: Upgrading your home’s safety features, such as replacing outdated plumbing or electrical systems, installing smoke detectors and carbon monoxide detectors, or reinforcing your roof, can lower your insurance costs. These improvements reduce the likelihood of claims.
- Shop around and compare quotes: Don’t settle for the first quote you receive. Compare prices and coverage from multiple insurers to find the best deal. Utilize online comparison tools to streamline this process.
Bundling Home and Auto Insurance
Bundling your home and auto insurance policies with the same company is a common and often effective way to save money. Insurers frequently offer significant discounts – sometimes exceeding 10% – for customers who bundle their policies. This is because managing multiple policies for a single customer is often more efficient for the insurance company.
For example, a homeowner paying $1,200 annually for home insurance and $800 annually for auto insurance might receive a 15% discount on the combined premium when bundling, resulting in savings of approximately $300 per year.
Improving Home Security to Reduce Insurance Costs
Implementing effective home security measures not only protects your property and family but can also lead to lower insurance premiums. Insurers recognize the value of proactive security and often reward homeowners who invest in these measures.
- Install a security system: A monitored security system, which alerts authorities in case of a break-in, is highly effective. Many insurers offer discounts for homes equipped with such systems.
- Reinforce exterior doors and windows: Stronger locks, reinforced frames, and security film on windows can deter intruders and reduce the risk of break-ins. These improvements can signal a lower risk to your insurer.
- Install exterior lighting: Well-lit areas around your home deter potential criminals and improve visibility, making it easier to identify suspicious activity.
- Use a smart home security system: Smart home devices, such as smart locks, security cameras, and motion sensors, offer advanced security features and can provide additional discounts with some insurance providers.
Final Review
Successfully navigating the world of home insurance requires understanding the interplay between coverage, cost, and your individual circumstances. By carefully considering the factors discussed—location, home features, coverage levels, and provider choices—you can secure a policy that provides adequate protection without breaking the bank. Remember to regularly review your policy and shop around to ensure you’re getting the best value for your money. Proactive planning and informed decision-making are key to achieving peace of mind and financial security.
FAQ
What is the difference between an HO-3 and an HO-5 policy?
An HO-3 (special form) covers your home against most perils except those specifically excluded. An HO-5 (comprehensive form) provides broader coverage, including personal property against a wider range of perils.
How often should I shop for home insurance?
It’s advisable to compare quotes annually or every other year to ensure you’re getting the best rates. Insurance markets fluctuate.
Can I lower my premiums by making home improvements?
Yes, upgrades like new roofing, security systems, and fire-resistant materials can often lead to lower premiums. Check with your insurer about specific discounts.
What happens if I file a claim?
Filing a claim may impact your future premiums, depending on the specifics of the claim and your insurer’s policies. Your rates could increase or your policy could be non-renewed.