Understanding average car insurance payments is crucial for navigating the complexities of auto insurance. This guide delves into the multifaceted factors influencing premiums, providing a clear picture of what shapes your individual cost. From geographic location and vehicle type to driving history and coverage choices, we explore the key elements that contribute to the final price tag.
We’ll examine how different insurance companies approach pricing, highlighting variations in their weighting of these factors. By understanding these nuances, you can make informed decisions to secure the most suitable and cost-effective coverage for your needs.
Factors Influencing Average Car Insurance Payments
The average cost of car insurance is not a fixed number; it varies significantly depending on a multitude of interconnected factors. Understanding these factors empowers consumers to make informed decisions and potentially secure more favorable insurance rates. This section will delve into the key elements that insurance companies consider when calculating premiums.
Age and Driving Experience
Age is a significant predictor of risk for insurance companies. Younger drivers, particularly those under 25, statistically have a higher incidence of accidents and traffic violations. This increased risk translates to higher premiums. As drivers gain experience and a clean driving record, their premiums generally decrease. Insurance companies use sophisticated actuarial models that incorporate age and years of driving experience to assess risk profiles. For example, a 20-year-old with a clean record might pay significantly more than a 40-year-old with a similar driving history. The perceived risk diminishes as drivers accumulate years of accident-free driving.
Driving History
A driver’s history is arguably the most crucial factor influencing insurance premiums. Accidents, speeding tickets, and other moving violations directly reflect a driver’s risk profile. Multiple incidents or serious offenses will substantially increase premiums. Conversely, a clean driving record can lead to significant discounts. Insurance companies maintain detailed records of driving infractions and accident claims, using this data to calculate individual risk scores. A single at-fault accident, for instance, can raise premiums for several years, even if the driver is otherwise considered low-risk.
Vehicle Type
The type of vehicle insured also significantly impacts premiums. Generally, newer, more expensive cars command higher premiums due to their higher repair costs and potential for greater losses in case of an accident or theft. Sports cars and high-performance vehicles are often associated with higher risk and thus higher premiums than more economical sedans or hatchbacks. The vehicle’s safety features also play a role; cars with advanced safety technology may qualify for discounts. Insurance companies utilize detailed databases of vehicle specifications and repair costs to assess the risk associated with each vehicle type.
Location
Geographic location is another critical factor. Areas with higher rates of theft, accidents, or vandalism will typically have higher insurance premiums. Urban areas, for example, often have higher premiums than rural areas due to increased traffic density and higher likelihood of collisions. Insurance companies analyze claims data by zip code and other geographic identifiers to determine risk levels in different locations. Living in a high-crime area will likely result in higher premiums than living in a low-crime area, even if all other factors remain constant.
Coverage Levels
The level of coverage selected significantly impacts the cost of insurance. Comprehensive and collision coverage, while offering more protection, are more expensive than liability-only coverage. Higher coverage limits (e.g., higher liability limits) also translate to higher premiums. Consumers can adjust their coverage levels to balance cost and protection, but opting for minimal coverage leaves them more vulnerable to financial losses in case of an accident. The choice of coverage is a trade-off between risk mitigation and premium cost.
Table: Relative Impact of Factors on Insurance Premiums Across Age Demographics
| Factor | 16-25 Year Olds | 26-35 Year Olds | 36-55 Year Olds | 56+ Year Olds |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | High Impact | Medium Impact | Low Impact | Medium Impact |
| Driving History | Very High Impact | High Impact | High Impact | High Impact |
| Vehicle Type | Medium Impact | Medium Impact | Medium Impact | Medium Impact |
| Location | Medium Impact | Medium Impact | Medium Impact | Medium Impact |
Geographic Variations in Average Car Insurance Payments
Car insurance premiums aren’t uniform across the United States; significant variations exist depending on location. These differences stem from a complex interplay of factors, primarily relating to risk assessment and the cost of providing insurance services in different areas. Understanding these variations is crucial for consumers seeking the best rates.
Geographic location is a major determinant of your car insurance costs. Several key factors contribute to this disparity, creating a complex landscape of premiums across the country.
Factors Contributing to Geographic Variations in Car Insurance Premiums
Several interconnected factors influence the average cost of car insurance across different geographic regions. These factors are often intertwined and work in concert to create higher or lower premiums.
Population density plays a significant role. More densely populated areas, such as major cities, generally have higher accident rates due to increased traffic congestion and driver interaction. This increased risk translates into higher insurance premiums for drivers in these areas. Conversely, sparsely populated rural areas tend to have lower accident rates and therefore lower premiums.
Accident rates are directly correlated with insurance costs. States and regions with high accident rates, often linked to factors like aggressive driving habits or poor road conditions, experience higher premiums. Insurance companies assess risk based on historical accident data, and areas with frequent accidents bear the brunt of higher premiums to offset the increased payout risk.
The cost of living, particularly healthcare costs, significantly impacts insurance premiums. States with high healthcare costs will naturally see higher insurance premiums, as the cost of treating injuries sustained in accidents is a major component of insurance payouts. This is because insurance companies must factor in the cost of medical expenses when setting premiums.
The cost of vehicle repairs also varies geographically. Areas with higher labor costs or a limited supply of auto parts may lead to increased repair expenses, consequently impacting insurance premiums. This is especially true for states with unique regulations or specialized repair needs.
Illustrative Map of Average Car Insurance Premiums
Imagine a map of the United States. The states are color-coded to represent the average annual car insurance premium. Deep red states indicate the highest premiums, perhaps exceeding $2000 annually. These states might be concentrated in the Northeast and along the coasts, reflecting higher population density, accident rates, and cost of living. States shaded in lighter shades of red, orange, and yellow represent progressively lower premiums, ranging from $1500 to $2000. The central and some southern states might fall into these categories. Finally, states shaded in light green and blue represent the lowest premiums, potentially below $1500 annually, often located in less populated areas of the Midwest and South. This color gradient provides a visual representation of the significant geographic disparity in average car insurance payments. The map clearly demonstrates that location is a significant factor affecting the cost of insurance.
Average Car Insurance Payments by Vehicle Type
The cost of car insurance isn’t solely determined by your driving record; the type of vehicle you drive significantly impacts your premiums. Different vehicles present varying levels of risk to insurance companies, leading to a wide range in average insurance payments. Factors like repair costs, likelihood of theft, and safety features all play a crucial role.
Understanding these differences can help you make informed decisions when choosing a car and planning your budget. The following sections detail how the type of vehicle you own directly influences your insurance premiums.
Vehicle Type and Insurance Premium Comparison
Several factors contribute to the disparity in insurance premiums across different vehicle types. Primarily, the cost of repairs after an accident is a major consideration. Luxury vehicles and those with complex technological features often require more expensive parts and specialized labor, driving up repair costs. Conversely, the simpler mechanics of some economy cars translate to lower repair bills. Theft rates also play a significant role; vehicles with high theft rates naturally command higher premiums. Finally, safety ratings, as determined by organizations like the IIHS and NHTSA, influence premiums; vehicles with superior safety features tend to have lower premiums due to a reduced likelihood of accidents and lower severity of injuries.
- Sedans: Sedans generally fall into the mid-range for insurance premiums. Repair costs are moderate, theft rates are relatively average, and safety ratings vary widely depending on the make and model. Expect premiums to be lower than SUVs or trucks but potentially higher than smaller, less powerful cars.
- SUVs: Sport Utility Vehicles often command higher premiums than sedans due to their larger size, higher repair costs (especially for bodywork), and sometimes higher theft rates for certain models. However, advancements in safety technology in many newer SUVs can offset this to some degree, resulting in a range of premiums.
- Trucks: Pickup trucks typically have higher insurance premiums than sedans or SUVs. Their larger size and weight increase the potential for damage in accidents, leading to higher repair costs. They also tend to have a higher rate of theft, especially for certain models. Additionally, some truck models may have lower safety ratings compared to other vehicle types.
- Sports Cars: Sports cars are notorious for having the highest insurance premiums. These vehicles are often expensive to repair, have higher theft rates due to their desirability, and may have lower safety ratings than more practical cars. The higher performance capabilities also increase the risk of accidents.
- Minivans/Compact Cars: Minivans and compact cars typically fall on the lower end of the insurance premium spectrum. Their smaller size, lower repair costs, and generally lower theft rates contribute to this. Many newer models also boast strong safety ratings.
Impact of Coverage Levels on Average Car Insurance Payments
The cost of car insurance is significantly influenced by the level of coverage selected. Choosing between minimum coverage requirements and more comprehensive plans directly impacts your premium. Understanding this relationship is crucial for making informed decisions about your insurance needs and budget. Higher coverage levels generally mean higher premiums, but they also provide greater financial protection in the event of an accident.
Your car insurance premium is a reflection of the risk the insurance company assumes. The more comprehensive your coverage, the higher the potential payout for the insurer, leading to a higher premium. Conversely, opting for minimal coverage limits the insurer’s potential liability and, consequently, reduces the premium. Adding optional features further modifies the cost, adding layers of protection and, therefore, expense.
Relationship Between Coverage Levels and Premiums
The level of coverage you choose directly correlates with your average car insurance payment. Minimum coverage, typically mandated by state law, provides basic liability protection, covering injuries or damages you cause to others. Collision and comprehensive coverage, however, are optional and significantly increase the premium. Collision coverage protects your vehicle in accidents regardless of fault, while comprehensive coverage protects against non-collision damage such as theft or weather-related events. Therefore, a policy with only liability coverage will be substantially cheaper than one offering full coverage (liability, collision, and comprehensive).
Impact of Optional Coverage Features
Adding optional coverage features, such as uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage, roadside assistance, rental car reimbursement, or medical payments coverage, increases the overall cost of your insurance. These add-ons provide additional protection and convenience but come at an extra price. For example, uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage protects you if you’re involved in an accident with a driver who lacks sufficient insurance. Roadside assistance covers towing and other emergency services. The cost of these add-ons varies depending on the insurer and the specific features included.
Average Premiums for Different Coverage Combinations
The following table illustrates how different coverage combinations affect average premiums. These are illustrative examples and actual premiums will vary based on factors like driving history, location, vehicle type, and the specific insurance company.
| Coverage Type | Liability Only (State Minimum) | Liability + Collision | Full Coverage (Liability, Collision, Comprehensive) | Full Coverage + Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Annual Premium (Example) | $500 | $800 | $1200 | $1400 |
Average Car Insurance Payments Over Time
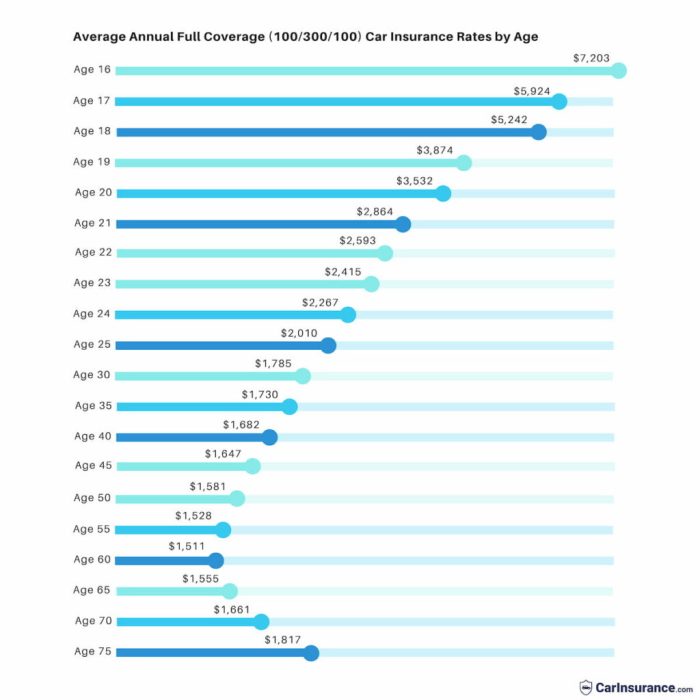
The cost of car insurance, like many aspects of life, isn’t static. Over the past decade, average premiums have fluctuated, influenced by a complex interplay of economic and societal factors. Understanding these trends is crucial for consumers to budget effectively and make informed decisions about their insurance coverage.
The average cost of car insurance has generally shown an upward trend over the past 5-10 years, though the rate of increase has varied from year to year. Several factors contribute to this trend, and it’s important to note that regional and individual variations exist.
Economic and Societal Factors Influencing Car Insurance Costs
Several interconnected factors contribute to the rising cost of car insurance. Inflation plays a significant role, increasing the cost of repairs and replacement parts for vehicles. Simultaneously, advancements in vehicle technology, while offering safety improvements, also mean more expensive repairs when accidents occur. Increased healthcare costs, resulting from more severe injuries in accidents, further contribute to higher insurance premiums. Furthermore, changes in claims frequency and severity, influenced by factors such as increased traffic congestion and distracted driving, also impact insurance pricing. Finally, legislative changes and regulatory requirements can influence the cost of insurance coverage.
Illustrative Line Graph of Average Car Insurance Payments
Imagine a line graph with “Year” on the horizontal (x) axis, ranging from 2014 to 2024. The vertical (y) axis represents “Average Annual Premium” in US dollars. The line itself would generally show an upward trend, although not necessarily a consistently steep incline. For example, we might see data points like these (these are illustrative and not actual data):
* 2014: $1200
* 2015: $1250
* 2016: $1280
* 2017: $1300
* 2018: $1350
* 2019: $1400
* 2020: $1420 (Slight decrease due to reduced driving during pandemic lockdowns)
* 2021: $1480
* 2022: $1550
* 2023: $1600
* 2024: $1650 (Projected)
The graph would visually demonstrate the general upward trend, with a slight dip potentially visible around 2020 reflecting the impact of reduced driving during the pandemic. The overall picture, however, highlights the increasing cost of car insurance over the decade. The specific numbers would vary depending on the source data and geographic location.
Comparison of Average Car Insurance Payments Across Insurance Providers
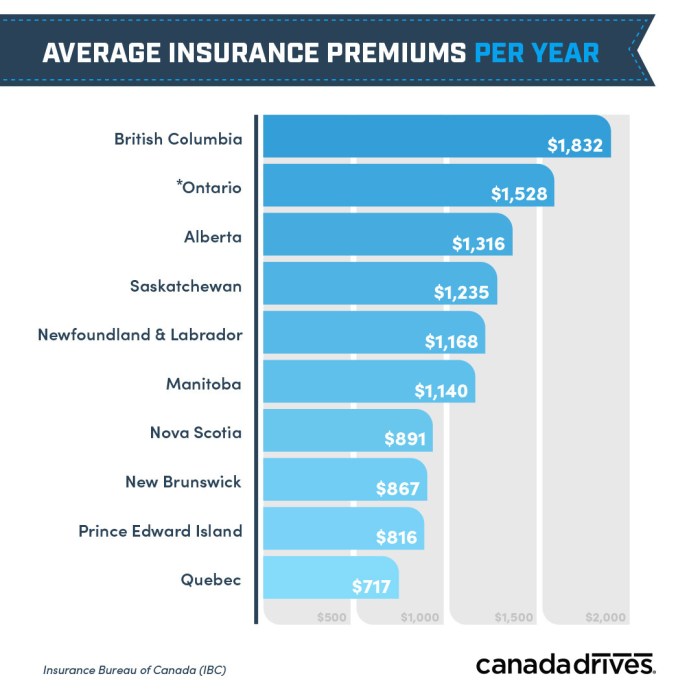
Understanding the variations in average car insurance payments across different providers is crucial for consumers seeking the best value for their money. Several factors contribute to these differences, leading to a wide range of premiums even for similar coverage levels and driver profiles. This comparison focuses on illustrating these differences and exploring some of the underlying reasons.
Differences in pricing among major insurance providers stem from a variety of factors. These include the provider’s risk assessment models, claims handling processes, administrative costs, marketing strategies, and the specific coverage options offered. Providers with more sophisticated risk assessment tools might be able to offer lower premiums to low-risk drivers, while those with higher administrative costs might need to charge more to maintain profitability. Furthermore, the level of customer service and the types of discounts available also influence the final premium.
Average Car Insurance Payments by Provider
The following table compares average annual car insurance payments for a hypothetical 30-year-old driver with a clean driving record, driving a mid-sized sedan, and carrying liability coverage. These are illustrative examples and actual premiums will vary significantly based on individual circumstances. Remember that these are averages and individual quotes will differ.
| Insurance Provider | Average Annual Payment | Key Coverage Features | Notable Discounts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Provider A (e.g., Geico) | $1200 | Standard liability, collision, comprehensive | Good driver discount, multi-car discount |
| Provider B (e.g., State Farm) | $1350 | Standard liability, collision, comprehensive, roadside assistance | Bundled home and auto discount, safe driver discount |
| Provider C (e.g., Progressive) | $1100 | Standard liability, collision, comprehensive, accident forgiveness | Good student discount, telematics discount |
| Provider D (e.g., Allstate) | $1400 | Standard liability, collision, comprehensive, rental car reimbursement | Multi-policy discount, defensive driving discount |
Closing Notes
Ultimately, the average car insurance payment is not a static figure; it’s a dynamic reflection of numerous individual circumstances. By carefully considering the factors discussed – your driving record, vehicle type, location, and desired coverage level – you can better anticipate your own insurance costs and proactively manage them. This understanding empowers you to shop effectively and secure the best possible insurance protection at a price that aligns with your budget.
Helpful Answers
How often are car insurance rates reviewed?
Insurance rates are typically reviewed annually, but can be adjusted more frequently based on changes in your driving record or policy details.
Can I get a discount for bundling insurance policies?
Yes, many insurers offer discounts for bundling car insurance with other policies, such as homeowners or renters insurance.
What is a SR-22 form?
An SR-22 form is a certificate of insurance that proves you have the minimum required auto insurance coverage. It’s often required by states after a serious driving offense.
What is the difference between liability and collision coverage?
Liability coverage pays for damages you cause to others, while collision coverage pays for damage to your own vehicle, regardless of fault.