The attempt to distinguish true Mullein from its botanical look-alike brothers uncovers a botanical journey full of almost invisible differences. Pioneering through woodland realms and open meadows, this exploration will highlight those distinctive features that set Mullein apart from amongst other botanical kinship. But beyond appearances, explore the subtle realm of medicinal applications and folklore concerning these green look-alike relatives.
Mullein and Its Look-Alike Plants
There are a few different ways in which Verbascum thapsus, or mullein, differs from its look-alike plants. First, the leaves have a covering of fuzz that provides a soft, velvety feel. This separates the mullein plahttps://houseofplants.biz.id/nt from other similar plants without this distinctive leaf covering.
These leaves grow in a whorl, usually at or very near ground level, forming almost a round cluster at the base of the plant. This pattern is helpful for distinguishing it from plants bearing alternate leaf arrangements or an altogether different growth form. Paying attention to this might help in accurate identification.
In observing mullein in relation to look-alike species, attention should be brought to habits of growth and general height the plant attains. Mullein is a tall-foraging plant that often reaches or tops 6 feet in height. It bears an unusual, single stalk topped by a spike of yellow flowers. This upright habit of growth and flower structure will serve to help differentiate mullein from other plants with similar foliage that present different flowering characteristics.
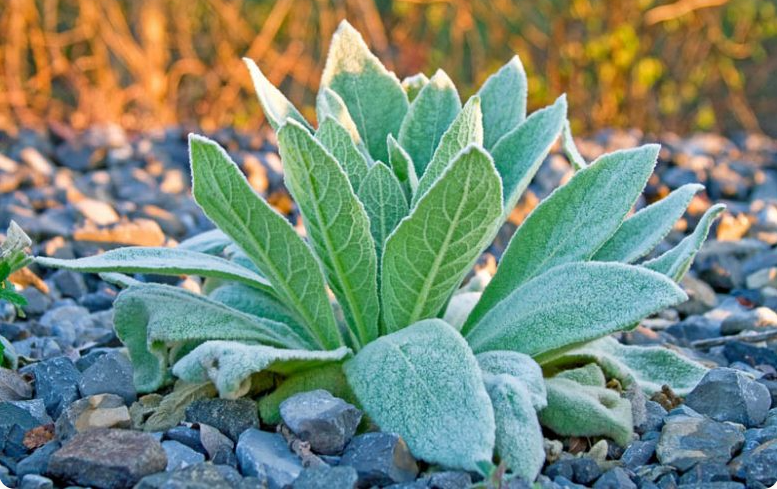

Mullein Leaves Identification Features
The leaves are normally of a velvety feel and broader than long, mostly having a distinctive appearance. Leaves are often in a basal rosette, averaging about 5 to 15 centimeters wide. Because they are very soft and fuzzy, they are quite different from many other leaves.
Besides that, the leaves of mullein are pale green in color with toothed margins, further making them quite different in their appearance. Because of their fuzzy outside, the leaves feel smooth to the touch, adding a sensory feature to help identify them among other leaves that look similar in most of their natural habitats.
One can also distinguish the leaves of mullein by noting its spiral arrangement along the stem. This adds to the plant’s general growth structure and ensures that mullein is differentiated from any similar species, which may have its leaves in an alternate arrangement. Plant look-alikes, in their natural habitat, can be correctly identified with the help of these features while foraging or studying plants.
Various Habits of Mullein Look-Alikes may easily pass for this polymorphic plant due to their general resemblance in appearance. It is very important to learn the differences so one is not confused and incorrectly identifies various species in different habitats.
Woodland Areas may host plants such as Common Mullein, Verbascum thapsus, which bear a resemblance in appearance to Mullein. However, notice specific things like the shape and texture of the leaves; Mullein generally has softer, fuzzy leaves compared to look-alikes.
Fields and Meadows harbor a great deal of different plants with characteristics that greatly resemble Mullein. Be watching for related species like Great Mullein Verbascum densiflorum or Dark Mullein Verbascum nigrum, which share characteristics but differ in flower color or growth habits, respectively.
While look-alike Mulleins are common in many habitats, paying attention to differences in leaf arrangement and flower structure will lead to correct identification. For specific details beyond what is provided in field guides, local botanists can provide additional ways to distinguish Mullein from similar plants.
Similar Plants of the Woodland
The plants that look like mullein can sometimes be deceiving in woodland areas because of their similar growth patterns and leaf structure. One common plant similar to the true mullein in such habitats is the Great Mullein, Verbascum thapsus, with its tall spire-like appearance and soft, fuzzy leaves much like the true mullein. However, the distinguishing feature between the two will be in their coloration and texture of leaves.
Common Mullein Verbascum sinuatum can also be found in wooded areas and can sometimes confuse onlookers. While both share general similarities in plant morphology, the texture of the leaves often remains different; where common mullein is often smooth, the leaves of true mulleins have a velvety feel. In such cases, careful observation of the traits of the leaf becomes quite crucial for correct identification.
Another common woodland area look-alike is the Common Mallow, Malva sylvestris. This plant, while soft-leaved and lobed, can easily appear as mullein from a distance with its tall stem. However, it does not take much closer inspection to realize that it is actually quite different in form and growth pattern from the true mulleins. Proper comparison of leaves helps in effective plant identification within the woodland setting.
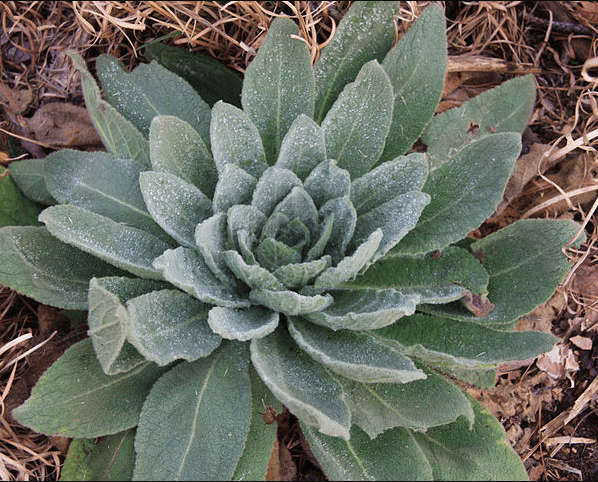

Look-Alikes Found in Meadows and Fields
There are a number of plants that might easily be mistaken for mullein because they often grow in meadows and fields. One is the common evening primrose, a tall plant with brilliant yellow flowers. Agrimony plant also tends to grow in these areas but consists of spiky yellow flowers and may resemble a mullein.
Moth mullein is similar to true mullein in general appearance when on meadow sites. This weed has a very thin stalk, and its flowers may be yellow. Teasel also has tall pointed flowers and sometimes appears in a field setting. General appearances of this type are similar to mullein, and correct identification needs to be obtained.
In the main, identification of mullein in meadows and fields should be very attentive to the form of leaves, coloring of flowers, and general growth habit in order to distinguish it from all other similar species. Knowing what characteristic features the plant has will contribute to eliminating its look-alike plants when sighted in nature.
Identifying Mullein Flowers among Similar Species
The flowers of mullein are distinguishable because of their notable features among others of their kind. Mullein flowers grow tall spikes with multiple small, yellow blossoms that bloom from bottom to top. This makes them unique in their vertical flowering pattern against other look-alikes within the plant kingdom.
The flowers of mullein are one identifying feature because of how dense the blooms are on the spike, creating that vibrant display. Other similar species may have different arrangements, with flowers or coloration other than the characteristic yellow coloring of the blossoms of mullein. This floral arrangement is an important feature that has to be considered for proper identification.
Besides, the shape and structure of flowers of mullein also constitute another important part of the differentiation process. Most usually, a common standard mullein flower takes a tubular shape of the flower with very delicate, yet minute petal parts which add more elegance to the flower. Observing the certain minute details about the flower anatomy, including petal shape and structure, botanists and naturalists differentiate mullein from its look-alike counterparts in nature.
Key Differences in Mullein and Similar Medicinal Plants
Mullein’s uniqueness from other medicinal plants lies in its very particular healing properties; though mullein as a herb is valued in respiratory ailments such as cough and bronchitis, some of its look-alike plants may not be used for these purposes. The other distinctive remedial applications of mullein make gaining full knowledge of its therapeutic value important, which is vital for realizing its optimal potentials in herbal drugs.
Besides, the extra caution taken in harvesting mullein for medicinal purposes makes it different from other species. Proper identification of the mullein plant ensures its safety and efficiency. Unlike other similar species, mullein requires some unique harvesting to maintain its medicinal efficacy and avoid possible side effects. This is what makes correct identification important in herbal medication.
Furthermore, folkloric uses across various cultures demonstrate the myriad purposes of mullein compared to other look-alike plants. From ear infections to skin irritations, mullein has been observed to offer a wide range of therapeutic applications that may not be represented in any similar species. Examining the rich history of the uses of mullein underlines its versatility and emphasizes its importance in nature-based therapies.
Traditional Uses and Healing Properties
Mullein, having soft leaves and towering height, has been in use for ages because of the plethora of medicinal properties. Traditionally, it was used to alleviate coughs and bronchitis that come with respiratory disturbances. The leaves of mullein are often put into use for herbal concoctions or teas for relieving congestion and addressing respiratory health.
In addition, mullein has been known for anti-inflammative, which has made it an herbal medication to treat conditions related to the sore throat, infection of the ear, amongst others. Also, mullein provides soft diuretic action; this helps the kidneys and facilitates detoxification within the body. These are also attributed to its emollient properties, which further extend their advantages in treating skin conditions such as burns and wounds.
In herbal medicine, mullein is a highly respected plant for its potential to soothe discomfort and promote general well-being. Appropriately harvested and processed, mullein is a legitimate botanical product that could be very useful to anyone interested in symptom relief with alternative therapies. Knowledge of traditional uses and healing properties of mullein furthers the importance of this plant in herbal practice and wholeness.
Precautions in Harvesting for Herbal Purposes
When harvesting mullein or any other medicinal plant for herbal purposes, there is a need to take caution on sustainability and safety. Following are some of the key precautions to be taken into consideration:
- Ethics in harvesting: Observe ethical practices of gathering mullein plants only in abundant populations and without harming the entire ecosystem.
- Timing: The best time to collect mullein leaves and flowers is during the peak season of the plant, when the plant has reached its best medicinal value. This is usually during the summer months.
- Identification: Correct identification of the mullein plant is very necessary to avoid the accidental collection of some look-alike species that may be toxic or less desirable for herbal purposes.
- Methods: Practices should be appropriate to avoid contamination by ensuring clean, sharp tools, and assurance of not collecting from polluted areas.
Further Resources for Learning and Plant Identification
For those desiring to learn more about wild mullein and the look-alike plants, there is much helpful information available. Most botanical field guides on either wildflowers or medicinal plants have detailed descriptions and images that help distinguish the mullein from similar species. Information from botanical websites, forums, and social media groups related to the identification of plants will also prove very helpful for both enthusiasts and botanists with discussions, photos, and expert views on mullein and its look-alikes.
Moreover, several botanical gardens and nature centers often organize workshops, seminars, or guided tours that introduce beginners to plant identification, including ordinary plants like mullein and their look-alikes. These classes or workshops provide real-life exposure and hands-on guidance in identifying the characteristic features of plants and understanding their role in the ecosystem they occur in. Local herbalist classes or workshops may also provide an opportunity to discuss the identification and uses of mullein and its look-alikes, examining both traditional uses and contemporary uses that have evolved for these plants as herbal medicines.
Additionally, there are online databases and university botanical websites, which give comprehensive profiles of plants for study, including morphology, distribution, and ecological significance. With the use of these resources, one can build upon this basic knowledge in botany by refining plant identification techniques and appreciating the diversity of plant life, including mullein and those that bear a close resemblance to it visually. Further research and exposure to these resources will provide full details on the principles of plant identification and aid in the conservation of the native species, like mullein, among its look-alike species.
Accordingly, distinguishing mullein from its look-alike plants is, therefore, of the highest importance to both foragers and herbalists. These key points involve the shape of its leaves, the structure of flowers, and growth habitats, which will embolden any individual in the process of identification of this very useful herb while it grows in the wild. Continue to practice more about identifying plants in order to harness benefits associated with mullein.
Remember, deep knowledge about mullein and its lookalike species is just what will ensure that your foraging is not only safe but will also enhance your understanding of the traditional uses and their healing properties. Take to the field with relevant knowledge about these plants in order to maximize their medicinal values. Have a great day out, and may the encounters with mullein and its lookalikes enrich your knowledge and practice in herbalism.