Navigating the complexities of Medicare can be daunting, but understanding your options is crucial for securing affordable and comprehensive healthcare coverage. AARP, a trusted name in senior advocacy, offers a range of Medicare plans designed to meet diverse needs and budgets. This guide delves into the specifics of AARP Medicare insurance plans, providing a clear and concise overview to help you make informed decisions about your healthcare future.
From understanding the different plan types and their associated costs to navigating the enrollment process and accessing customer support, we aim to equip you with the knowledge necessary to choose the AARP Medicare plan that best aligns with your individual circumstances. We’ll explore the benefits and limitations of each plan, compare them to other Medicare options, and address frequently asked questions to ensure a thorough understanding.
AARP Medicare Plan Overview
AARP Medicare plans, offered by UnitedHealthcare, are Medicare Advantage plans designed to provide comprehensive healthcare coverage to AARP members. These plans offer a variety of options to suit different needs and budgets, combining the benefits of Original Medicare with additional features. Understanding the nuances of each plan is crucial to making an informed decision about your healthcare coverage.
AARP Medicare Plan Types and Eligibility
AARP offers several types of Medicare Advantage plans, primarily Medicare Advantage (Part C) plans, which are offered through private insurance companies. These plans differ in their coverage specifics, costs, and the level of network restrictions. Eligibility for any AARP Medicare plan requires enrollment in both Medicare Part A (hospital insurance) and Part B (medical insurance). You must also reside in the plan’s service area. Specific plan availability varies by location.
AARP Medicare Plan Benefits and Coverage
AARP Medicare Advantage plans generally cover the same services as Original Medicare (Part A and Part B), including doctor visits, hospital stays, and some preventive services. However, many plans offer additional benefits not covered under Original Medicare, such as vision, hearing, and dental coverage. Some plans also include prescription drug coverage (Part D), which is typically a separate plan under Original Medicare. The specific benefits and coverage will vary depending on the chosen plan and your location. It’s important to review the plan’s evidence of coverage (EOC) for detailed information.
AARP Medicare Plan Comparison
The following table provides a comparison of key features for different example AARP Medicare plans. Remember that plan details, including premiums and deductibles, can change annually, and availability varies by location. It’s crucial to check the most up-to-date information directly with AARP or UnitedHealthcare.
| Plan Name | Premium | Deductible | Coverage Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|
| AARP Medicare Complete (Example Plan A) | $0-$50 (Example) | $0-$500 (Example) | Covers Part A & B, plus vision, dental, hearing; may include Part D |
| AARP Medicare Advantage (Example Plan B) | $25-$75 (Example) | $0-$200 (Example) | Covers Part A & B, may include additional benefits like telehealth; Part D may be separate |
| AARP Medicare Select (Example Plan C) | $10-$40 (Example) | $100-$300 (Example) | Covers Part A & B; limited network; may have lower premiums; Part D may be separate |
| AARP Medicare Essentials (Example Plan D) | Variable (Example) | Variable (Example) | Focuses on essential coverage, often with lower premiums but potentially higher out-of-pocket costs; Part D may be separate |
AARP Medicare Plan Costs and Premiums
Understanding the costs associated with an AARP Medicare plan is crucial for making an informed decision about your healthcare coverage. These plans, offered by UnitedHealthcare, offer various options, each with its own pricing structure. It’s important to remember that costs can vary significantly depending on several factors, which we will explore below.
AARP Medicare plans, like other Medicare Advantage plans, involve several cost components. These include monthly premiums, which are the regular payments you make for your coverage; deductibles, which are the amounts you pay out-of-pocket before your plan begins to cover expenses; and co-pays, which are fixed amounts you pay for specific services, like doctor visits or prescriptions. The specific costs will depend on the plan you choose, your location, and your healthcare needs.
Factors Influencing AARP Medicare Plan Costs
Several factors significantly influence the overall cost of an AARP Medicare plan. These factors interact to create a unique cost profile for each individual.
Your age plays a role, though not as directly as other factors. While age is a factor in general health insurance pricing, AARP plans primarily focus on the specific plan benefits and your geographic location. Your location, however, is a major determinant. The cost of healthcare services varies considerably across different regions of the country, impacting plan premiums and out-of-pocket expenses. Finally, your health status is a key factor. Individuals with pre-existing conditions or anticipated higher healthcare utilization may find that plans with lower premiums but higher out-of-pocket costs are less advantageous. Conversely, those expecting lower healthcare usage might opt for plans with lower monthly premiums but higher deductibles and co-pays.
Example Cost Comparison for a 65-Year-Old
The following table illustrates potential cost differences between various hypothetical AARP Medicare plans for a 65-year-old individual residing in a specific region. Remember that these are examples and actual costs will vary based on the specific plan details, location, and network providers.
| Plan Name | Monthly Premium | Annual Deductible | Doctor Visit Co-pay |
|---|---|---|---|
| AARP Plan A | $25 | $1500 | $30 |
| AARP Plan B | $40 | $0 | $20 |
| AARP Plan C | $60 | $0 | $10 |
| AARP Plan D | $15 | $2000 | $40 |
Note: This table provides a simplified comparison. Actual costs may include additional charges depending on the specific services received and the plan’s benefit structure. Always consult the plan’s summary of benefits and coverage for complete details.
AARP Medicare Plan Networks and Providers

Choosing an AARP Medicare plan involves understanding its network of participating healthcare providers. The specific doctors, hospitals, and other healthcare facilities included in your plan’s network will vary depending on the plan you select and your geographic location. It’s crucial to verify coverage before seeking care to avoid unexpected out-of-pocket expenses.
AARP Medicare plans utilize a network of providers, meaning that you’ll generally pay less for care if you use in-network providers. The size and scope of these networks differ between plans. Some plans offer broader networks, including a wider selection of doctors and hospitals, while others have more limited networks. The implications of choosing a plan with a limited network are primarily financial; using out-of-network providers will typically result in significantly higher costs for your services. You may face higher copayments, coinsurance, and deductibles, potentially leading to substantial out-of-pocket expenses.
Identifying Participating Providers and Hospitals
AARP Medicare plans provide resources to help members easily identify in-network providers. Their websites usually feature online provider directories, searchable by specialty, name, and location. These directories offer detailed information about each provider, including their contact details, address, and accepted plan types. Additionally, members can contact AARP’s customer service directly for assistance in locating nearby in-network providers. Many plans also offer mobile apps that provide similar search capabilities, allowing for quick and convenient access to provider information on the go. For example, a member in Phoenix, Arizona, searching for a cardiologist could use the online directory to find all participating cardiologists within a specified radius of their home address.
Implications of Choosing a Plan with a Limited Network
Selecting an AARP Medicare plan with a limited network can significantly impact healthcare costs. While these plans may offer lower premiums, the trade-off is often reduced provider choice. If your preferred doctor or specialist isn’t in the network, you’ll likely face substantially higher out-of-pocket expenses when receiving care. For instance, a routine checkup with an out-of-network physician could cost hundreds of dollars more compared to seeing an in-network physician. This difference becomes even more pronounced for more complex medical procedures or extended hospital stays. Careful consideration of your healthcare needs and preferred providers is essential before enrolling in a plan with a limited network.
Finding In-Network Doctors and Specialists
Finding in-network doctors and specialists is a straightforward process.
- Use the online provider directory: Most AARP Medicare plans offer a searchable online directory on their website. This directory allows you to search by specialty, name, location, and other criteria.
- Utilize the AARP Medicare plan mobile app (if available): Many plans offer mobile apps with similar search functionalities, providing convenient access to provider information.
- Contact AARP customer service: If you need assistance navigating the online directory or have questions about finding in-network providers, contact AARP’s customer service department for personalized help.
- Check your plan’s materials: Your plan’s welcome packet or member handbook may include a list of participating providers in your area.
- Ask your current doctor: If you have an existing relationship with a doctor, inquire whether they participate in the AARP Medicare plan you’re considering.
Enrollment and Switching AARP Medicare Plans
Choosing and managing your AARP Medicare plan requires understanding the enrollment process and procedures for switching plans. This section details the steps involved in both enrolling in a new plan and switching from one AARP Medicare plan to another, including important deadlines and considerations.
The enrollment and switching processes for AARP Medicare plans are governed by specific timeframes and regulations. Understanding these processes is crucial to ensure continuous and uninterrupted Medicare coverage. Failure to adhere to deadlines can result in gaps in coverage or limitations on plan choices.
AARP Medicare Plan Enrollment
Enrolling in an AARP Medicare plan typically involves several key steps. The initial enrollment period depends on your circumstances. For those initially eligible for Medicare, there’s a seven-month Initial Enrollment Period (IEP) centered around your 65th birthday. Special enrollment periods exist for specific circumstances, such as job loss or moving. Outside these periods, enrollment may be subject to penalties.
- Determine Eligibility and Plan Options: Before beginning the enrollment process, verify your eligibility for Medicare and research available AARP Medicare plans to find one that best suits your needs and budget.
- Gather Necessary Information: You will need your Medicare card, Social Security number, and other relevant personal information to complete the application.
- Complete the Application: Applications can often be completed online, by phone, or through a licensed insurance agent. Carefully review all information before submitting.
- Confirm Enrollment: After submitting your application, you should receive confirmation of your enrollment and effective date.
Switching AARP Medicare Plans
Switching between AARP Medicare plans is possible during specific enrollment periods. The Annual Enrollment Period (AEP) typically runs from October 15th to December 7th, allowing for changes to take effect January 1st of the following year. Special circumstances may also qualify you for a Special Enrollment Period (SEP), allowing for a switch outside of AEP. It’s important to carefully compare plans and understand the potential consequences of switching before making a decision.
- Review Available Plans: During the AEP or SEP, compare available AARP Medicare plans to identify a suitable alternative.
- Compare Benefits and Costs: Carefully review the coverage, premiums, deductibles, and co-pays of each plan.
- Submit a Change Request: Contact AARP or your insurance provider to initiate the plan change process, typically through their website or by phone. Provide the necessary information to complete the request.
- Confirm the Change: Once the change is processed, you will receive confirmation of your new plan and effective date.
AARP Medicare Plan Customer Service and Support
Accessing reliable and responsive customer service is crucial for navigating the complexities of Medicare plans. AARP Medicare plans offer various support channels designed to assist members with questions, concerns, and plan-related issues. These options aim to provide timely and effective solutions, ensuring a positive member experience.
AARP Medicare plans provide comprehensive customer service options to address member needs. These options are designed to offer flexibility and convenience, allowing members to choose the method that best suits their preferences and circumstances.
Available Customer Service Options
Members can access support through multiple channels, including a dedicated phone number staffed by knowledgeable representatives available during extended hours. A user-friendly online portal provides access to account information, claims status, and helpful resources. Email support offers a convenient written communication option for less urgent inquiries. In some cases, mail correspondence may also be used for certain requests or clarifications. The availability and specifics of each channel may vary depending on the specific AARP Medicare plan.
Resources and Support Provided to Plan Members
Beyond direct contact, AARP Medicare plans offer a wealth of self-service resources to empower members to manage their care. The online portal provides detailed plan information, including formularies, provider directories, and explanations of benefits. Educational materials, such as brochures and online tutorials, address common Medicare questions and plan-specific details. The website also often features frequently asked questions (FAQs) sections addressing many common issues. Dedicated phone lines for specific issues, such as prescription drug assistance or appeals processes, are often available.
Examples of Common Issues Resolved by AARP Medicare Customer Service
Customer service representatives regularly assist members with a wide range of inquiries. Common issues include clarifying plan benefits, understanding explanation of benefits (EOB) statements, locating in-network providers, resolving billing discrepancies, navigating the appeals process for denied claims, and obtaining information about prescription drug coverage and formularies. For instance, a member might call to confirm whether a specific doctor is in their plan’s network before scheduling an appointment, or to understand why a particular medication was not covered under their prescription drug plan. Another common scenario involves resolving billing questions, such as discrepancies between the bill received and the expected cost based on the plan’s coverage details. Customer service also plays a key role in guiding members through the appeals process if a claim is denied, ensuring they understand their rights and options.
Comparing AARP Medicare Plans to Other Medicare Options
Choosing the right Medicare plan can be complex, and understanding the differences between AARP plans and other options is crucial for making an informed decision. This section compares AARP Medicare plans with other Medicare Advantage plans, Original Medicare, and Medicare Supplement plans, highlighting key distinctions to aid your selection process.
AARP Medicare Plans Compared to Other Medicare Advantage Plans
AARP Medicare plans are Medicare Advantage plans offered by UnitedHealthcare. While they share many features with other Medicare Advantage plans—like offering Part A, Part B, and often Part D coverage—key differences exist. These differences often lie in specific plan details such as the provider network, prescription drug formularies, and the monthly premiums. Some AARP plans may offer additional benefits not found in other Medicare Advantage plans, such as vision, hearing, or dental coverage. Conversely, another Medicare Advantage plan from a different provider might offer better coverage for a specific condition or medication. Ultimately, the best plan depends on individual needs and preferences, requiring a thorough comparison of available options in your area.
AARP Medicare Plans Compared to Original Medicare
Original Medicare (Part A and Part B) differs significantly from AARP Medicare Advantage plans. Original Medicare is a fee-for-service program where you pay a portion of the costs for each service, while AARP Medicare Advantage plans typically have a monthly premium and a set cost-sharing structure for covered services. Original Medicare requires supplemental coverage (like Medigap) to avoid high out-of-pocket costs, whereas AARP Medicare Advantage plans often include prescription drug coverage (Part D) within the plan. Original Medicare offers broader access to providers nationwide, while AARP Medicare Advantage plans have a defined network. The choice depends on your healthcare needs, budget, and preference for managed care versus fee-for-service.
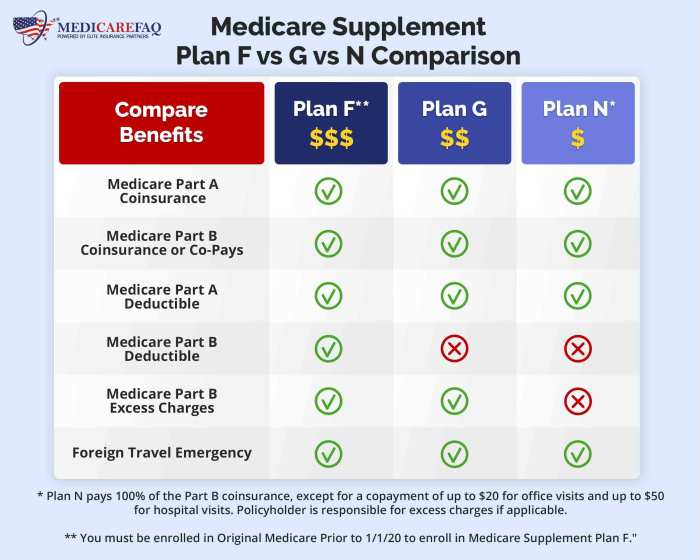
AARP Medicare Plans Compared to Medicare Supplement Plans (Medigap)
The following table summarizes the key differences between AARP Medicare Advantage plans and Medicare Supplement plans:
| Feature | AARP Medicare Advantage Plan | Medicare Supplement Plan (Medigap) | Key Difference Summary |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage | Part A, Part B, and often Part D; may include extra benefits | Helps pay Original Medicare’s cost-sharing | One integrates all parts, the other supplements Original Medicare. |
| Cost | Monthly premium; cost-sharing for services | Monthly premium; cost-sharing varies by plan | Both have premiums, but cost-sharing differs significantly. |
| Network | Limited network of providers | No network restrictions; can see any doctor who accepts Original Medicare | One restricts provider choice, the other offers more flexibility. |
| Prescription Drug Coverage | Often included (Part D) | Usually requires a separate Part D plan | One typically includes Part D, the other requires a separate plan. |
Understanding AARP Medicare Plan Exclusions and Limitations
AARP Medicare plans, while offering comprehensive coverage, do have certain exclusions and limitations. Understanding these is crucial for managing expectations and ensuring you receive the most benefit from your plan. It’s important to remember that these plans are supplemental to Original Medicare, and some services are simply not covered under any Medicare plan, including AARP’s offerings.
It’s essential to carefully review your specific plan’s Evidence of Coverage (EOC) document for a complete and accurate list of what is and isn’t covered. The information below provides a general overview of common exclusions and limitations, but should not be considered exhaustive.
Common Exclusions and Limitations
AARP Medicare plans, like other Medicare Advantage plans, generally exclude certain services or have limitations on coverage. These exclusions can vary based on the specific plan chosen and your individual circumstances. Understanding these potential gaps in coverage is key to avoiding unexpected medical expenses.
- Routine Vision Care: Most AARP Medicare plans do not cover routine eye exams, eyeglasses, or contact lenses. While some plans may offer limited coverage for vision care as a supplemental benefit, it’s usually minimal. For comprehensive vision care, you would typically need a separate vision insurance policy.
- Routine Hearing Care: Similar to vision care, routine hearing exams, hearing aids, and related services are generally not covered under AARP Medicare plans. Again, some plans might offer limited coverage as a supplemental benefit, but extensive hearing care typically requires a separate hearing insurance plan.
- Dental Care: Routine dental care, such as cleanings, fillings, and dentures, is typically excluded from AARP Medicare plans. Dental coverage is usually obtained through a separate dental insurance policy.
- Long-Term Care: AARP Medicare plans do not cover long-term care services, such as nursing home care or assisted living facilities. This type of care requires separate long-term care insurance.
- Cosmetic Procedures: Procedures deemed purely cosmetic, such as elective plastic surgery or non-medically necessary procedures, are not covered.
- Experimental Treatments: Medicare, including AARP Medicare plans, generally does not cover experimental or investigational treatments or procedures that haven’t been fully approved.
Situations Where Coverage Might Be Limited
There are several circumstances where AARP Medicare plan coverage may be less comprehensive than expected.
It’s important to note that even for covered services, cost-sharing such as deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance can significantly impact out-of-pocket expenses. The amount of cost-sharing varies depending on the specific plan and the type of service received. For instance, while a doctor’s visit might be covered, you may still be responsible for a copay. Similarly, while hospitalization might be covered, you might have a deductible and coinsurance to pay. Understanding these cost-sharing responsibilities is critical in managing your healthcare budget. Furthermore, if you receive care outside your plan’s network, you may face higher costs or even have services denied altogether.
Illustrative Scenario: AARP Medicare Plan Selection
Sarah, a 67-year-old retiree, recently became eligible for Medicare and is navigating the complexities of choosing a plan. She understands the importance of selecting a plan that aligns with her specific needs and budget. This case study illustrates her decision-making process.
Sarah’s primary concerns are keeping her healthcare costs manageable while ensuring access to her preferred specialists. She also wants a plan that offers comprehensive coverage and a user-friendly claims process.
Factors Considered in Plan Selection
Sarah meticulously evaluated several factors before making her decision. These included her budget constraints, her existing health conditions and the need for specific specialists, and the availability of those specialists within the plan’s network. She prioritized a balance between cost and comprehensive coverage.
Step-by-Step Decision-Making Process
First, Sarah created a detailed budget, outlining how much she could comfortably allocate monthly towards Medicare premiums and out-of-pocket expenses. She then researched several AARP Medicare Advantage plans, carefully comparing their premiums, deductibles, and co-pays. She noted which plans covered her existing medications and whether her preferred cardiologist and primary care physician were in-network.
Next, Sarah utilized the AARP Medicare plan finder tool online, inputting her zip code and other relevant information to narrow down her options based on her location. The tool provided a list of plans available in her area, along with detailed information on coverage, costs, and provider networks.
She then compared the plans side-by-side, focusing on those that fell within her budget and included her doctors. She meticulously examined the formularies (lists of covered medications) to ensure her prescription drugs were included. She also checked the plan’s customer service ratings and reviews to gauge the ease of accessing support if needed.
Finally, after carefully weighing the pros and cons of several plans, Sarah chose the AARP Medicare Advantage plan that best suited her needs and budget. This plan offered a good balance of cost-effectiveness, comprehensive coverage, and access to her preferred healthcare providers. The plan’s reasonable monthly premium and relatively low out-of-pocket costs were particularly appealing. The fact that her cardiologist and primary care physician were both in-network was a crucial factor in her final decision.
Final Wrap-Up
Choosing the right Medicare plan is a significant decision impacting your health and finances. This guide has provided a detailed exploration of AARP Medicare insurance plans, outlining their features, costs, and enrollment processes. By carefully considering your individual needs, budget, and healthcare preferences, you can confidently select the AARP plan that offers the best coverage and value, ensuring you receive the quality healthcare you deserve throughout your retirement years. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional or Medicare advisor for personalized guidance.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the difference between AARP Medicare Advantage and AARP Medicare Supplement plans?
AARP Medicare Advantage plans (Part C) are all-in-one plans replacing Original Medicare (Part A and B). AARP Medicare Supplement plans (Medigap) help pay for costs Original Medicare doesn’t cover.
Can I keep my current doctor if I switch to an AARP Medicare plan?
It depends on the plan. Medicare Advantage plans have networks; your doctor must be in-network for coverage. Medicare Supplement plans generally allow you to see any doctor who accepts Medicare.
When is the best time to enroll in an AARP Medicare plan?
You can enroll during the Annual Enrollment Period (AEP) from October 15th to December 7th, with coverage starting January 1st. There are also special enrollment periods for qualifying life events.
How do I file a claim with my AARP Medicare plan?
The claims process varies depending on the plan type. Some plans handle claims automatically, while others may require you to submit claims forms. Check your plan materials for specific instructions.