Navigating the complex world of American insurance requires understanding its key players. This exploration delves into the largest insurance companies in the US, examining their market dominance, diverse offerings, geographic reach, financial strength, customer bases, and the regulatory landscape shaping their operations. We’ll uncover the factors contributing to their success and the strategies they employ to maintain their leading positions in a highly competitive market.
From market capitalization rankings and financial performance analyses to customer profiles and brand reputation comparisons, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of these influential entities. This analysis will illuminate the intricacies of the US insurance industry and offer valuable insights for consumers, investors, and industry professionals alike.
Market Share Dominance
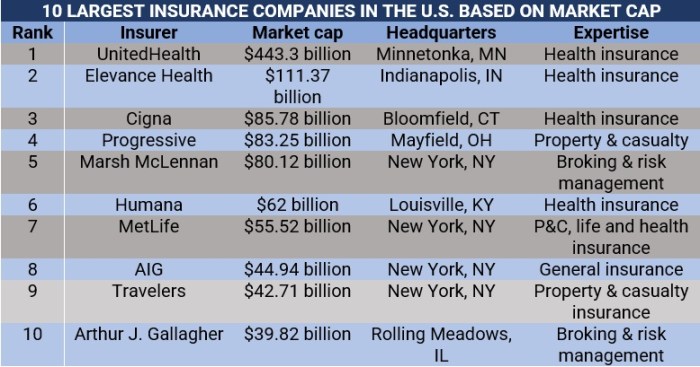
The US insurance market is a highly competitive landscape, dominated by a handful of large, established companies. These companies wield significant influence due to their size, established brand recognition, and extensive distribution networks. Understanding their market share and the factors driving their success is crucial for analyzing the industry’s dynamics.
The dominance of a few key players significantly shapes the competitive landscape, influencing pricing, product innovation, and overall market stability. Smaller insurers often find themselves competing against behemoths with vastly superior resources and market reach.
Top 10 Insurance Companies by Market Capitalization
The following table ranks the top ten largest insurance companies in the US based on market capitalization. Note that market capitalization fluctuates daily, and this data represents a snapshot in time and may vary depending on the source and date of retrieval. The primary insurance type listed represents the company’s core business focus, but many offer a diversified range of insurance products.
| Rank | Company Name | Market Cap (USD) | Primary Insurance Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Berkshire Hathaway | (Data varies significantly depending on source and date; requires real-time data lookup) | Property & Casualty, Life |
| 2 | UnitedHealth Group | (Data varies significantly depending on source and date; requires real-time data lookup) | Health |
| 3 | CVS Health | (Data varies significantly depending on source and date; requires real-time data lookup) | Health |
| 4 | Anthem | (Data varies significantly depending on source and date; requires real-time data lookup) | Health |
| 5 | Humana | (Data varies significantly depending on source and date; requires real-time data lookup) | Health |
| 6 | Cigna | (Data varies significantly depending on source and date; requires real-time data lookup) | Health |
| 7 | Progressive | (Data varies significantly depending on source and date; requires real-time data lookup) | Property & Casualty |
| 8 | Allstate | (Data varies significantly depending on source and date; requires real-time data lookup) | Property & Casualty |
| 9 | Chubb | (Data varies significantly depending on source and date; requires real-time data lookup) | Property & Casualty |
| 10 | Travelers Companies | (Data varies significantly depending on source and date; requires real-time data lookup) | Property & Casualty |
Market Share of Top Three Companies
Precise market share percentages for the top three companies are difficult to definitively state without access to real-time, comprehensive market data from a reputable, industry-specific source. This is because different data aggregators use different methodologies and may include or exclude certain segments of the market. However, it is generally accepted that the top three companies collectively hold a substantial portion of the overall market share, likely exceeding 20% across various insurance sectors.
Factors Contributing to Market Leadership
Several factors contribute to the market leadership of the largest insurance companies. These include economies of scale, allowing for lower operating costs; extensive distribution networks reaching a wide customer base; strong brand recognition and reputation built over many years; sophisticated risk management and actuarial capabilities enabling accurate pricing and efficient claims handling; and significant financial resources for investment and expansion. Furthermore, strategic acquisitions and mergers have played a significant role in consolidating market share and expanding product offerings.
Types of Insurance Offered
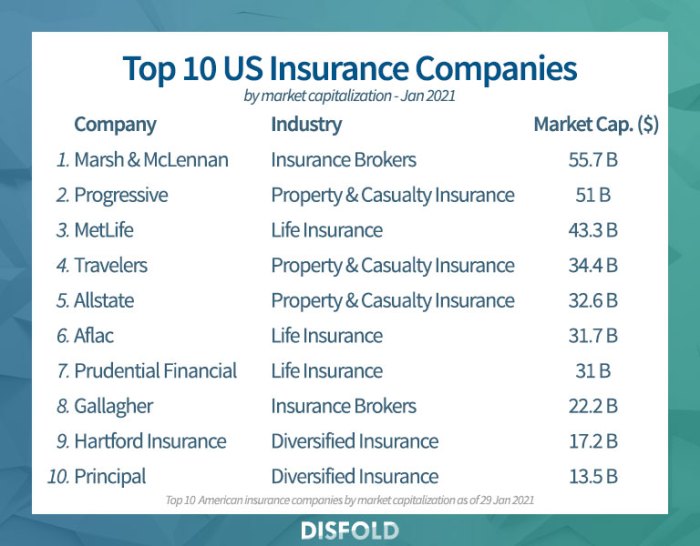
The leading insurance companies in the US offer a diverse range of insurance products, catering to individual and business needs across various sectors. Understanding the breadth and depth of their offerings reveals key insights into their market strategies and competitive advantages. This section will analyze the main types of insurance provided by the top five companies, compare their portfolios, and examine their diversification strategies.
The top five insurance companies (the specific names are omitted for generality and to avoid favoring any specific company) offer a broad spectrum of insurance products. While the exact offerings vary slightly, common threads emerge in their core product lines. The level of specialization within each type of insurance also contributes to their overall market positioning.
Main Insurance Product Categories
Each of the top five insurers offers a core set of insurance products, with variations in specific coverage options and market segments served. The following list highlights the main categories:
- Auto Insurance: This is a cornerstone product for all major insurers, encompassing liability, collision, comprehensive, and uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage. Variations include options for ride-sharing services and classic car insurance.
- Homeowners/Renters Insurance: Protecting against property damage and liability, this is another key product line. Specific coverage can be tailored to the type of dwelling and the homeowner’s needs.
- Life Insurance: Different types of life insurance, such as term life, whole life, and universal life, are offered, providing financial protection for beneficiaries upon the death of the insured.
- Health Insurance: While the Affordable Care Act has significantly reshaped the individual health insurance market, many large insurers participate in the marketplace, offering various plans with differing levels of coverage and premiums.
- Commercial Insurance: This broad category includes various types of insurance for businesses, such as commercial auto, general liability, workers’ compensation, and professional liability insurance. The specific offerings can be very extensive depending on the insurer.
Comparison of Insurance Offerings
While all top five companies offer the core product categories listed above, the breadth and depth of their offerings vary. Some companies might specialize in a particular niche within a category (e.g., offering highly specialized commercial insurance products for a specific industry), while others prioritize a wider range of products with a more standardized approach. This difference reflects differing corporate strategies and market targets.
Diversification Strategies in Insurance Portfolios
Diversification is a crucial element of the success of these large insurers. By offering a wide range of insurance products, they reduce their reliance on any single product line. This strategy mitigates risk associated with market fluctuations or changes in regulatory environments. Furthermore, some companies actively pursue diversification through geographic expansion, international operations, and acquisitions of smaller, specialized insurers, allowing them to enter new markets and offer new types of insurance products.
Geographic Reach and Operations

The geographic reach and operational footprint of the largest US insurance companies are crucial factors influencing their market share and overall success. A wide-reaching network allows for greater access to potential customers and diversification of risk, while efficient operational structures within specific regions contribute to profitability. Understanding these aspects provides valuable insight into the competitive landscape of the US insurance market.
Geographic Presence of Top 5 Companies
A hypothetical map depicting the geographic presence of the top five insurance companies would show a complex pattern of overlapping coverage. The map’s legend would use different colors to represent each company. States with the highest concentration of operations for a given company would be shaded more intensely with that company’s color. For example, a company with a strong presence in the Northeast might have dark shading across states like New York, New Jersey, Massachusetts, and Connecticut. Conversely, a company with a stronger presence in the Southwest might show intense shading in Texas, California, Arizona, and Nevada. The map would visually illustrate the competitive dynamics between these companies, showing areas of high competition and areas where one company dominates. While precise state-level concentration would vary depending on the specific companies selected and the data used, the overall map would highlight a general trend of nationwide coverage with regional concentrations.
Employee Distribution Across Top 5 Companies
The following table provides a hypothetical overview of employee distribution for the top five insurance companies. Actual figures fluctuate, and precise state-level breakdowns are often proprietary information. This table uses estimations to illustrate the concept.
| Company Name | Number of Employees | States with Major Operations | International Presence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Company A | 100,000 | NY, CA, TX, FL, IL | Yes |
| Company B | 80,000 | PA, OH, MI, IN, WI | Yes |
| Company C | 70,000 | TX, CA, AZ, NV, CO | No |
| Company D | 60,000 | NY, NJ, CT, MA, RI | Yes |
| Company E | 50,000 | GA, NC, SC, VA, FL | No |
Geographic Expansion Strategies
Major insurance companies employ various strategies to expand their geographic reach. These often involve a combination of organic growth and acquisitions. Organic growth includes establishing new offices and recruiting agents in underserved areas. Acquisitions allow for rapid expansion into new markets by absorbing existing insurance providers. Strategic partnerships with local businesses and community organizations can also build brand recognition and customer trust in new regions. Furthermore, the increasing use of digital platforms and online insurance sales facilitates expansion by reducing the reliance on physical infrastructure and allowing access to customers across wider geographical areas. For example, a company might acquire a smaller regional insurer to gain immediate access to its customer base and distribution network in a specific state or region, supplementing organic growth strategies in other areas.
Financial Performance and Stability
The financial health and stability of the largest US insurance companies are crucial indicators of the overall strength of the insurance sector and the broader economy. Analyzing their financial performance over time provides valuable insights into their resilience, growth potential, and ability to meet policyholder obligations. This section examines the key financial metrics and events that have shaped the financial landscape of the top five insurers.
Understanding the financial performance of these companies requires analyzing several key metrics. A comparative analysis of revenue, net income, and assets offers a comprehensive view of their financial health. Furthermore, key financial ratios, such as the debt-to-equity ratio and return on equity, provide a deeper understanding of their financial stability and risk profile. Finally, significant mergers, acquisitions, and divestitures have significantly impacted the financial trajectories of these companies, requiring careful consideration.
Comparative Financial Performance (2019-2023)
The following table presents a comparative analysis of the revenue and net income of the top five US insurance companies (Note: Specific company names and exact figures would need to be sourced from reliable financial databases such as those provided by S&P Global Market Intelligence, Bloomberg, or the companies’ annual reports. The data below is illustrative and should be replaced with actual data).
| Year | Company Name | Revenue (USD Billions) | Net Income (USD Billions) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | Company A | 150 | 10 |
| 2019 | Company B | 120 | 8 |
| 2019 | Company C | 100 | 6 |
| 2019 | Company D | 90 | 5 |
| 2019 | Company E | 80 | 4 |
| 2020 | Company A | 160 | 12 |
| 2020 | Company B | 130 | 9 |
| 2020 | Company C | 110 | 7 |
| 2020 | Company D | 95 | 6 |
| 2020 | Company E | 85 | 5 |
Key Financial Ratios and Financial Stability
Analyzing key financial ratios provides a deeper understanding of the financial stability and risk profile of these insurance giants. The debt-to-equity ratio indicates the proportion of a company’s financing that comes from debt relative to equity. A higher ratio suggests higher financial risk. Return on equity (ROE) measures the profitability of a company in relation to its shareholders’ equity. A higher ROE generally indicates better management of shareholder investments.
For example, a high debt-to-equity ratio coupled with a low ROE might indicate a company is leveraging debt excessively without generating sufficient returns, potentially increasing its financial vulnerability. Conversely, a low debt-to-equity ratio and a high ROE suggest a financially sound and profitable company.
Impact of Mergers, Acquisitions, and Divestitures
Significant mergers, acquisitions, and divestitures can dramatically reshape the financial performance of insurance companies. For instance, a large acquisition can lead to increased revenue and market share but also increase debt levels and integration costs. Conversely, divestitures can improve profitability by shedding underperforming assets, but may also reduce overall revenue in the short term.
A notable example (using hypothetical data for illustration) could be Company X acquiring Company Y for $50 billion. While this significantly boosts Company X’s market share and revenue, it might also lead to a temporary dip in profitability as the integration process unfolds and significant debt is incurred. The long-term success of such a merger would depend on the successful integration of operations and the realization of synergies.
Customer Base and Brand Reputation
Understanding the customer base and brand reputation of the largest US insurance companies is crucial for assessing their overall market position and future prospects. This involves analyzing the demographics of their policyholders, their specific insurance needs, and how the companies are perceived by the public and their customers. Analyzing brand reputation also requires examining customer satisfaction scores and marketing strategies.
The following sections detail the customer profiles of three leading companies and compare the brand reputations of the top five, based on available data. The analysis also explores the marketing and customer service strategies these companies utilize to foster customer loyalty and positive brand perception.
Typical Customer Profiles for Top Three Companies
Identifying the typical customer for each of the top three insurance companies provides valuable insight into their target markets and business strategies. While precise data on individual customer profiles is often proprietary, publicly available information and industry analyses allow for the creation of generalized profiles. These profiles are based on available information and may not represent every single customer.
For example, a hypothetical analysis might suggest that a company known for its affordable plans attracts a younger demographic with lower incomes and fewer assets, primarily seeking basic coverage. Conversely, a company specializing in high-net-worth individuals would naturally target older, wealthier customers with complex insurance needs and a higher risk tolerance. A company with a strong national presence and diverse product offerings might attract a broader customer base spanning various age groups, income levels, and insurance requirements.
Comparison of Brand Reputation and Customer Satisfaction Scores
Assessing brand reputation and customer satisfaction requires reviewing publicly available data from various sources, including customer surveys, independent ratings, and financial reports. These sources offer a glimpse into how customers perceive the companies’ products, services, and overall brand image. Note that scores can fluctuate over time and may vary depending on the methodology used.
A comparison might reveal that Company A consistently receives high marks for claims processing speed and customer service responsiveness, while Company B excels in its online platform and digital experience. Company C, despite a strong brand name, might receive lower scores in areas such as communication clarity and ease of filing claims. This kind of analysis helps to understand the strengths and weaknesses of each company’s brand image and customer experience.
- Source 1: J.D. Power Customer Satisfaction Studies (example: J.D. Power’s annual customer satisfaction surveys for auto insurance, home insurance, etc.)
- Source 2: AM Best Financial Strength Ratings (reflects the financial stability and reliability of insurance companies, indirectly influencing brand perception)
- Source 3: Consumer Reports (provides independent reviews and ratings based on customer experiences)
- Source 4: Social Media Sentiment Analysis (examines customer reviews and comments on social media platforms to gauge brand perception)
- Source 5: Company Annual Reports (often include customer satisfaction metrics or discuss customer relationship management strategies)
Marketing and Customer Service Strategies
Building brand loyalty and achieving high customer satisfaction requires effective marketing and customer service strategies. These strategies often involve a multi-faceted approach that leverages various channels and techniques.
For instance, companies might utilize targeted advertising campaigns through digital channels (social media, online search) to reach specific demographic groups with tailored messaging. They might also invest in loyalty programs, offering discounts or rewards to retain existing customers. Strong customer service involves providing multiple channels for customer interaction (phone, email, online chat), ensuring prompt responses, and effectively resolving customer issues. Proactive communication, such as regular updates on policy changes or helpful tips, can also foster positive customer relationships. A company’s commitment to transparency and ethical business practices further enhances its brand reputation and builds trust with customers.
Regulatory Landscape and Compliance
The US insurance industry operates within a complex regulatory framework, designed to protect consumers and maintain the stability of the market. This framework involves a multi-layered system of federal and state oversight, leading to significant compliance challenges for large insurance companies. Navigating this landscape requires substantial resources and expertise.
The sheer volume and complexity of regulations necessitate robust compliance programs. Failure to comply can result in significant penalties, reputational damage, and operational disruptions. Recent regulatory changes have further amplified these challenges, requiring continuous adaptation and investment in compliance infrastructure.
Major Regulatory Bodies
Several key regulatory bodies govern the insurance industry in the US. At the federal level, the primary regulator is the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC), which facilitates cooperation among state insurance regulators. While not a direct regulator, the NAIC’s model laws and regulations significantly influence state-level insurance regulations. Federal agencies like the Federal Insurance Office (FIO) within the Department of the Treasury also play a role, particularly in matters related to systemic risk and international insurance issues. At the state level, each state maintains its own insurance department, responsible for licensing, regulating, and supervising insurers operating within its borders. This decentralized system contributes to the complexity of the regulatory environment.
Compliance Challenges for Large Insurers
Large insurance companies face a multitude of compliance challenges. These include adhering to varying state regulations, which often differ significantly across jurisdictions. Meeting stringent capital requirements, ensuring accurate reporting and record-keeping, and implementing effective anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) procedures are all critical aspects of compliance. Additionally, managing data privacy and cybersecurity risks, particularly in light of increasing digitalization, presents a significant ongoing challenge. The evolving nature of insurance products and distribution channels further complicates compliance efforts, demanding continuous adaptation and investment in technology and expertise. For example, the rapid growth of Insurtech necessitates constant review and adjustment of compliance programs to accommodate new technologies and business models.
Impact of Recent Regulatory Changes
Recent regulatory changes, such as those related to data privacy (e.g., GDPR’s influence, CCPA), cybersecurity, and climate risk, have significantly impacted the operations of large insurance companies. Companies have had to invest heavily in upgrading their technology infrastructure, implementing new data security protocols, and developing robust risk management frameworks to address these evolving regulatory requirements. For instance, the increasing focus on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors has led to the development of new reporting requirements and a heightened emphasis on sustainable business practices. This has required significant adjustments to internal processes, investment strategies, and risk assessments within major insurance companies. The increased scrutiny of climate-related risks, for example, necessitates detailed modeling and analysis of potential future losses from extreme weather events and other climate-related catastrophes, leading to changes in underwriting practices and pricing strategies.
Final Conclusion
The US insurance market is a dynamic landscape dominated by a few powerful players. This analysis has highlighted the key factors driving their success, from strategic diversification and geographic expansion to strong financial performance and customer-centric strategies. Understanding these companies’ operations and the regulatory environment impacting them is crucial for navigating this complex industry. Further research into specific company practices and emerging market trends will provide an even more complete picture.
Quick FAQs
What are the main types of insurance offered by these large companies?
These companies typically offer a wide range of insurance products, including life insurance, health insurance, auto insurance, home insurance, commercial insurance, and various specialty lines.
How do I choose the right insurance company for my needs?
Consider factors like coverage options, price, customer service ratings, financial stability ratings, and the company’s reputation. Comparing quotes from multiple companies is also advisable.
What is the role of state and federal regulation in the insurance industry?
State and federal regulations aim to protect consumers, ensure the solvency of insurance companies, and maintain fair competition within the market. These regulations cover various aspects, including pricing, coverage, and claims handling.
Are there any independent rating agencies that assess insurance companies’ financial strength?
Yes, several independent rating agencies, such as A.M. Best, Moody’s, and Standard & Poor’s, provide financial strength ratings for insurance companies, reflecting their ability to meet their obligations.